In this article, I’d like to give more focus on a powerful component in the Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) Architecture that will make an amazing shift in the RAN Automation world.
Open radio access networks promise to unlock massive innovation, creating new opportunities for service providers to deliver differentiated services to consumers, businesses, and governments.
What is the RIC?
A RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) is a software-defined component of the Open RAN architecture that’s responsible for controlling and optimizing RAN functions. The RIC is a critical piece of the Open RAN disaggregation strategy, bringing multivendor interoperability, intelligence, agility, and programmability to radio access networks. The RIC enables the onboarding of third-party applications that automate and optimize RAN operations at scale while supporting innovative use cases that lower mobile operators’ total cost of ownership (TCO) and enhance customers’ quality of experience (QoE).
What are the RIC Benefits?
The RIC brings intelligence, agility, and programmability to radio access networks and enables third-party applications that automate and optimize RAN operations at scale while supporting innovative use cases. It plays a key role in network functions like network slicing, high-bandwidth, low-latency applications, and prioritized communications.
Where is the RIC Position in the ORAN Architecture?
The O-RAN Alliance’s architecture extends the 3GPP’s open RAN architecture to further disaggregate the RAN and open it up to multiple vendors. As below figure, the O-RAN architecture splits the distributed unit (DU) of the 3GPP into a DU and a radio unit (RU) and also added the RIC in the heart middle of the architecture.
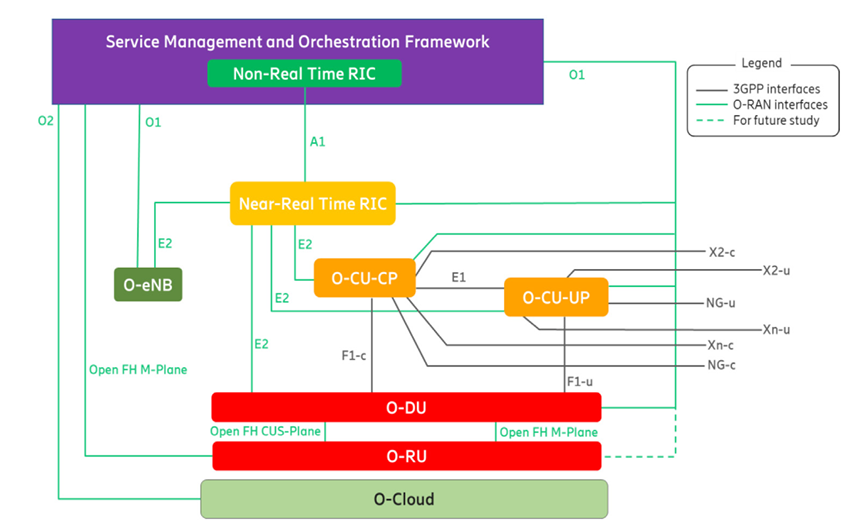
There are two logical forms of the RIC, and each performs a different function.
- The non-real-time RIC (Non-RT RIC) is part of the Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) Framework, centrally deployed in the service provider network. It enables greater-than-one-second control and policy guidance over the RAN elements and their resources through rApps.
- It also enables AI/ML capabilities for the RAN and uses long-term network data, such as performance metrics as well as enrichment data from external applications, to train and generate AI/ML-driven applications.
- The near-real-time RIC (Near-RT RIC) is a distributed RIC that runs extensible microservices from third-party vendors, called xApps by the O-RAN Alliance. It is responsible for fast loop control of the RAN network functions. It provides less-than-one second control over the RAN nodes and resources which are driven by the non-real-time RIC.
The Non-RT RIC communicates with the Near-RT RIC over an A1 interface to provide policy-based guidance to the xApps running on the Near-RT RIC to optimize RAN behavior, such as for capacity, customer-specific service levels, or energy efficiency. Many xApps and rApps will use open interfaces and machine learning to optimize RAN resources.
What are RIC Use Cases?
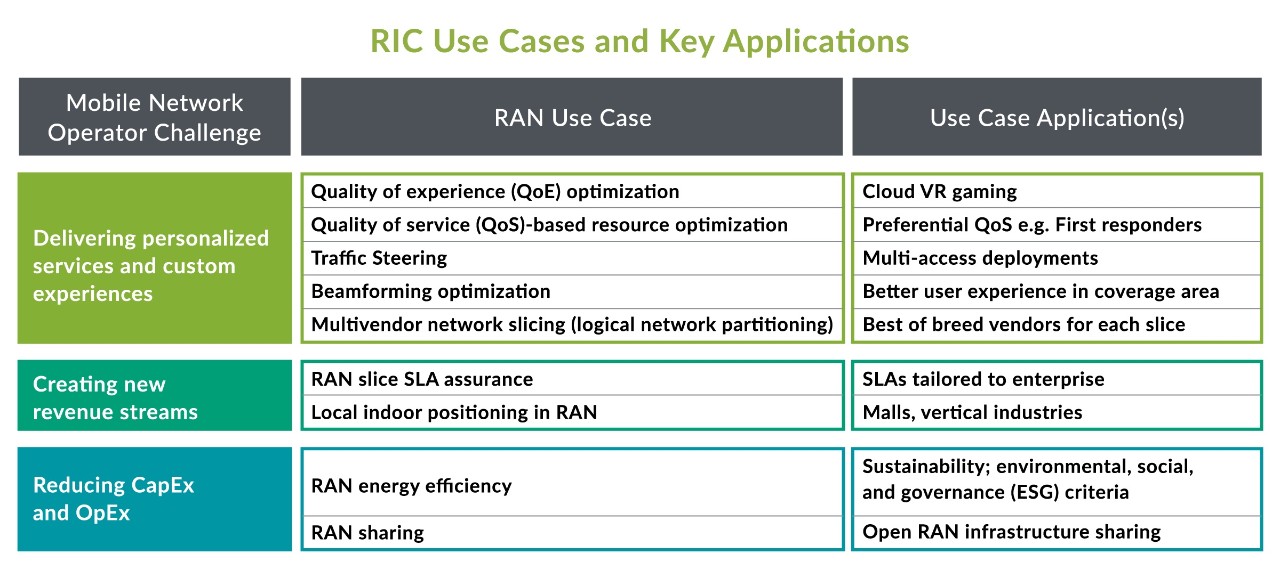
The RIC Use Cases can include different use cases, some of them are below:
- Massive MIMO optimization
- MU-MIMO allows simultaneous communication with multiple users in the same time and frequency slots, thereby allowing a cell to push more bits per time and frequency, thus improving the efficiency of the most valuable resource in the RAN which is the spectrum.
- PCI conflict and collision detection
- RIC can help in detecting physical cell identity (PCI) confusion and collisions during critical operator scenarios to speed up new cell deployments, drive faster times to market for new services, and improve the performance of existing cells.
- Subscriber QoS optimization
- Anomaly detection monitors subscriber-level trace information for every subscriber and uses AI to detect subscribers with anomalous QoS and generate alerts for subscribers with anomalous QoS.
- Traffic steering
- Traffic steering lets you manage traffic according to such objectives as network performance and cell load balancing to help improve access, quality of service, throughput, and performance.
- Traffic steering helps solve some problems like unbalanced loads among cells, cell groups, and bearers by routing, balancing, switching, and splitting traffic across diverse, multi-access radio networks.
