The architecture of eNB or gNB with O-DU and O-RUs has some important definitions here:
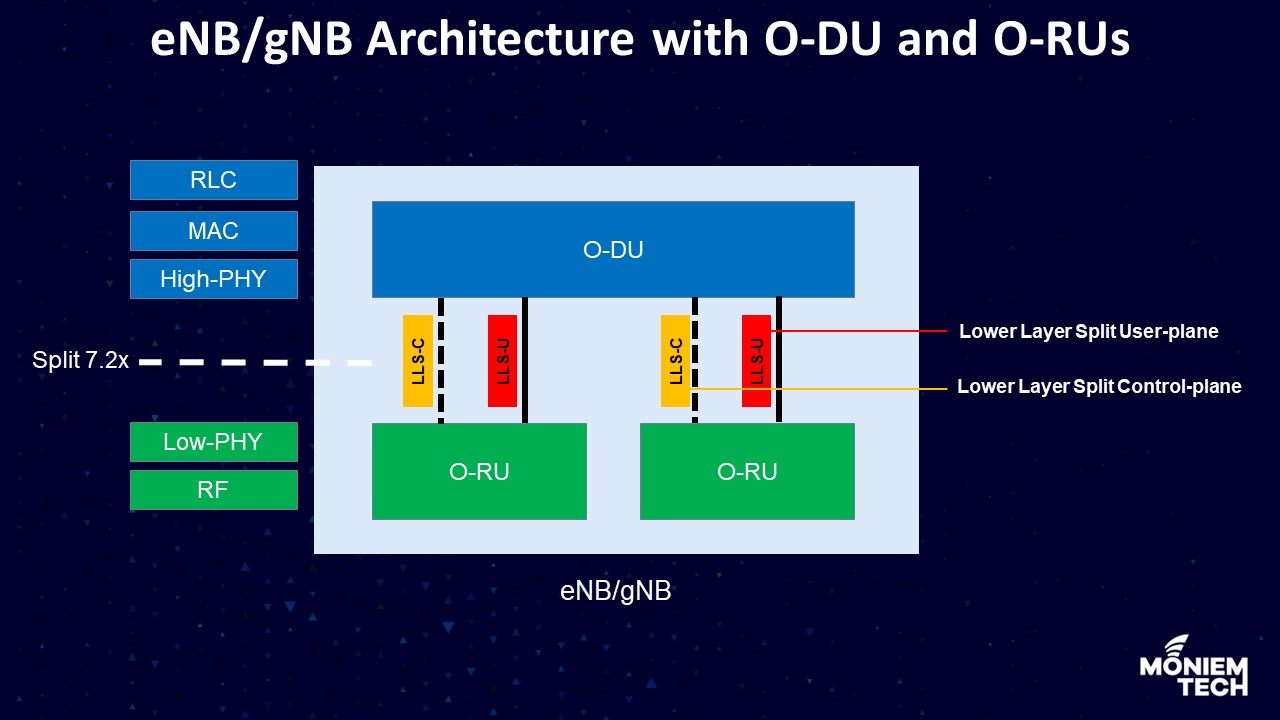
- O-DU: O-RAN Distributed Unit: a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer functional split.
- O-RU: O-RAN Radio Unit: a logical node hosting the Low-PHY layer and RF processing based on a lower layer functional split.
- LLS: Lower Layer Split: logical interface between O-DU and O-RU when using a lower layer (intra-PHY based) functional split.
- LLS-U: Lower Layer Split User-plane: logical interface between O-DU and O-RU when using a lower layer functional split.
- LLS-C: Lower Layer Split Control-plane: logical interface between O-DU and O-RU when using a lower layer functional split.
- High-PHY: those portions of the PHY processing on the O-DU side of the fronthaul interface, including FEC encode/decode, scrambling, and modulation/demodulation.
- Low-PHY: those portions of the PHY processing on the O-RU side of the fronthaul interface, including FFT/iFFT, digital beamforming, and PRACH extraction and filtering.
Split 7.2x Function
When considering the functional split defining a fronthaul interface there are two competing interests:
- There is a benefit in keeping an O-RU as simple as possible because size, weight, and power draw are primary deciding considerations, and the more complex an O-RU, the larger, heavier, and more power-hungry the O-RU tends to be.
- There is a benefit in having the interface at a higher level which tends to reduce the interface throughput relative to a lower-level interface – but the higher-level the interface, the more complex the O-RU tends to be.
To resolve this debate, O-RAN has selected a single split point, known as “7-2x” but allows a variation, with the precoding function to be located either “above” the interface in the O-DU or “below” the interface in the O-RU.
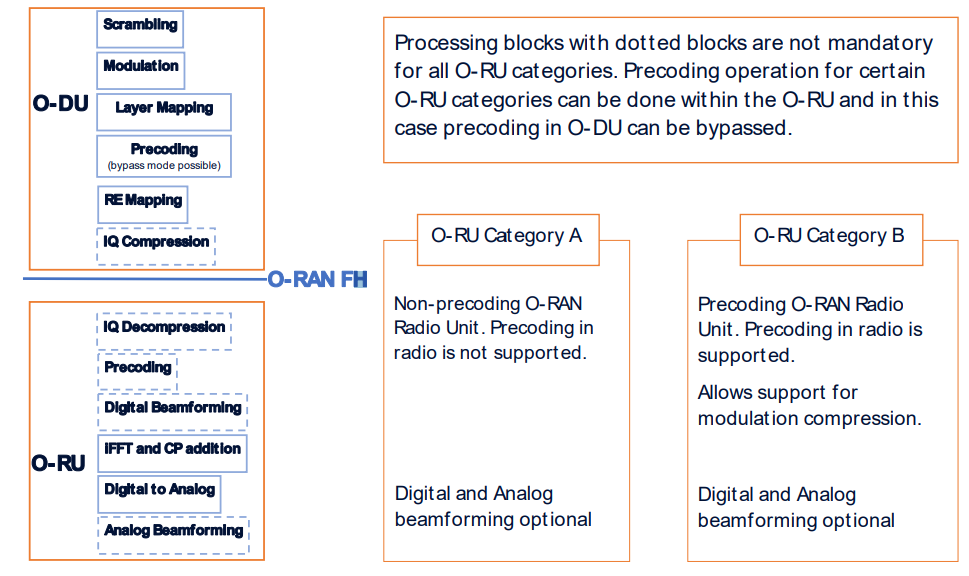
- O-RUs within which the precoding is not done (therefore of lower complexity) are called “Category A” O-RUs.
- O-RUs within which the precoding is done is called “Category B” O-RUs.
