The open radio access network or Open RAN can be broadly divided into the following three elements:
-
Open interfaces that combine RAN equipment from a variety of vendors.
-
Virtualization (i.e., virtualized RAN (vRAN) that enables hardware and software inside RAN equipment to be separated.
-
Intelligent control that optimizes and automates RAN operation.
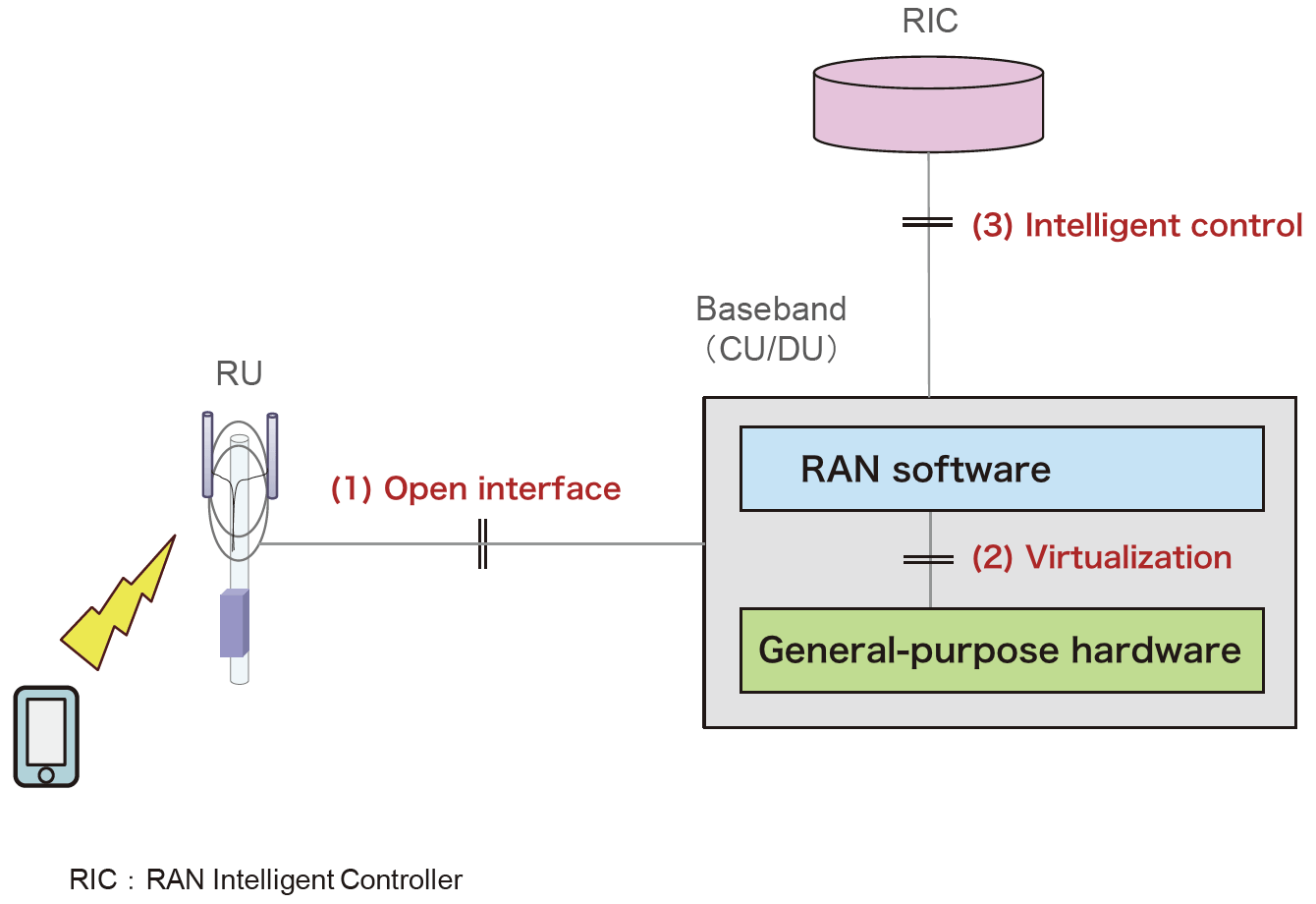
Open RAN can be separated into multiple components—Radio Unit (RU), Distributed Unit (DU), and Central Unit (CU)—each of which can be connected via standardized interfaces.
For telecom operators, this means that they can free themselves from vendor lock-in, shorten the time to commercial deployment, and adopt a better equipment configuration to provide optimized services to consumers. In addition, the virtualization of RAN means that costs can be decreased through the use of general-purpose hardware and that flexibility and scalability can be enhanced. Furthermore, envisioning an increasingly complex mobile network in the future, manual operation of the network as has been the practice so far will become all the more difficult, but this problem can be solved through the intelligent control of RAN.
In short, these three elements are essential to meeting the demand for a more diverse RAN industry and supporting an increasingly complex mobile system.
Reference: NTT Docomo
