Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), the successor to Wi-Fi 6, introduces the 6GHz frequency band, doubling the maximum frequency bandwidth from 160MHz to 320MHz.
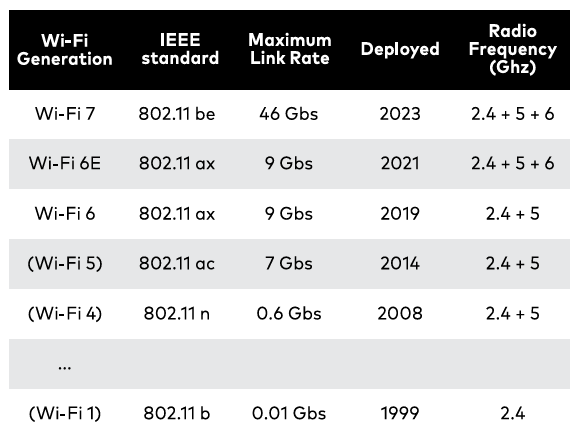
It allows the 16×16 MIMO configuration and supports 4096QAM modulation technology, which offers significant improvements in data rates, capacity, and spectral efficiency, ultimately enhancing the performance and user experience in wireless communication systems. With a maximum data transfer rate of 46Gbps, Wi-Fi 7 is nearly 4.8 times faster than Wi-Fi 6.
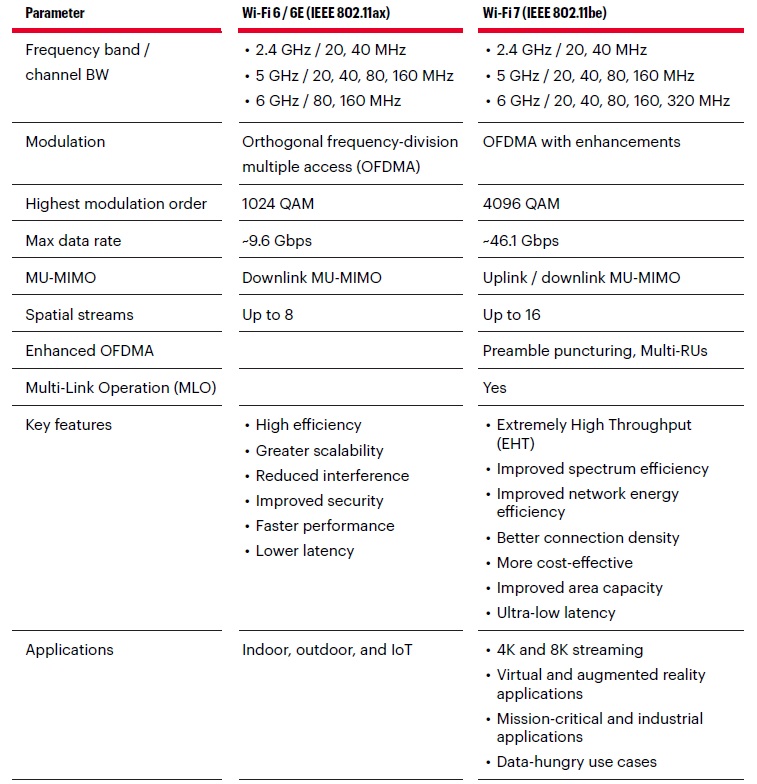
- The IEEE 802.11be standard, or Wi-Fi 7, builds on the foundation laid by its predecessor, Wi-Fi 6 / 6E, to deliver even faster and more reliable connectivity.
- The 320 MHz channel bandwidth of Wi-Fi 7 in the 6 GHz band provides a wider channel to transmit more data. WiFi 7 uses puncturing to partition the spectrum into usable portions. While channel puncturing existed in Wi-Fi 6 as an optional feature, it is becoming a standard feature with Wi-Fi 7.
- Wi-Fi 7 allows a maximum of 4096 QAM, 4K QAM, with 12 data bits per symbol.
- Wi-Fi 7 will introduce Multi-Link Operation (MLO) technology, which allows devices to send and receive data over multiple frequency bands simultaneously using a single aggregated connection. The aggregated connection can include signals from any of the three bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz.
