VoWiFi, or Voice Over WiFi, is an IMS Voice Call made through WiFi without using a cellular network like LTE or NR. It is similar to VoLTE (Voice over LTE) or VoNR (Voice or NR), the only difference is the type of communication channel being used for the IMS voice call. WiFi channel (instead of LTE or NR) is used for VoWiFi.
There’s a special node for security and authentication purposes between the Un-Trusted non-3GPP network (WiFi) and the Mobile Core network (EPC) which is called: ePGD or Evolved Packet Data Gateway (ePDG).
What is ePGW?
The ePDG is a crucial component in VoWiFi technology. It enables secure connections between untrusted non-3GPP IP access networks, like Wi-Fi, and trusted mobile networks. It establishes IPsec tunnels to ensure secure communication, facilitating seamless voice and data services over Wi-Fi.
What are the main differences between VoWiFi and VoLTE?
The main difference between VoWiFi and regular IMS/SIP voice calls (e.g., VoLTE or VoNR) is the procedure happening before the IMS/SIP procedure.
In the case of VoWiFi, the following unique procedure happens #before IMS/SIP voice call establishment:
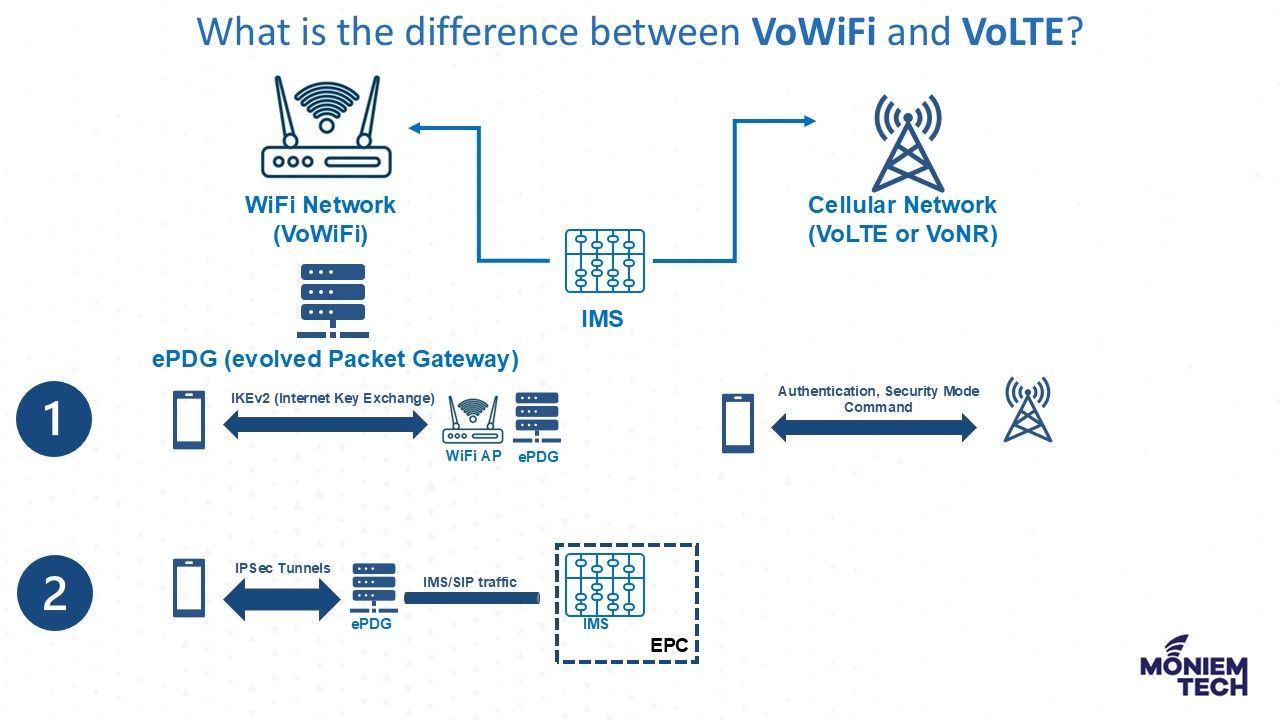
1. IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange): This is a handshake procedure to authenticate and set security to ePDG. It is equivalent to the Authentication and Security Mode Command procedure in a cellular network (e.g., LTE, or NR network).
2. Establishing IPSec Tunnels: UE and ePDG establish IPsec tunnels based on the security settings configured during IKE, through which IMS/SIP traffic is going through.
