Before discussing ePDG in more detail, let’s explain why we need it. The answer is to connect between 3GPP networks (LTE/5G core) and non-3GPP networks (Wi-Fi). But, why do we need to interconnect between them?
Imagine you’re walking in the street and making a call, suddenly you arrive at your office and need to park your car in the underground parking. However, you’re afraid to continue the call due to the cellular network’s bad coverage in the parking. Here the interconnection between cellular network and WiFi is essential. The main idea of interconnection between 3GPP and non-3GPP or WiFi is to expand mobile networks’ coverage and service potential.
Key to the VoWiFi technology is a series of architectural elements, protocols, and interfaces that enable calls to be carried end-to-end across networks using different technologies and with different owners. The most important is the Evolved Packet Data Gateway (ePDG).
This vital component enables connectivity between mobile networks and non-3GPP networks, such as public Wi-Fi, commonly used for offloading data and voice traffic. With the increasing number of Wi-Fi hotspots and the need for flexible mobile services, the ePDG is crucial in improving network coverage, security, and user experience.
What is The Evolved Packet Data Gateway (ePDG) ?
The ePDG is a network element designed for secure access and interworking between 3GPP networks (LTE/5G core) and non-3GPP networks (Wi-Fi). It acts as a security gateway, creating a secure connection from untrusted networks to the mobile core network. This connection is achieved through an IPsec tunnel, ensuring data is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
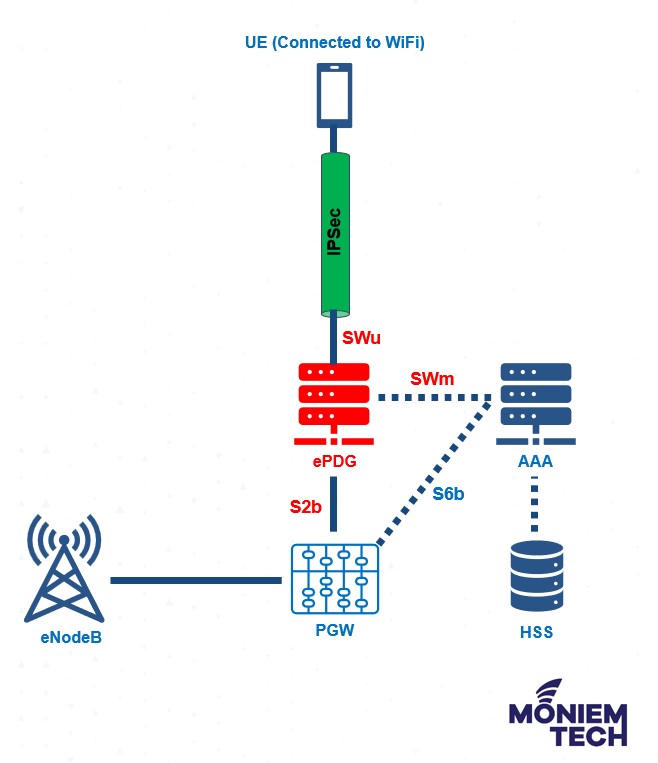
ePDG Benefits and Key Features
- Secure Connectivity: Implements IPsec tunnels to securely connect user equipment (UE) over untrusted WiFi to the operator’s core network and encrypts data to ensure secure communication.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces reliance on costly cellular infrastructure by leveraging existing WiFi networks.
- Seamless Handoff: Supports seamless handoff between LTE and WiFi networks, enhancing user experience and continuity during calls or data sessions.
- Data Offloading: Offloads traffic from cellular networks to WiFi, reducing congestion and operational costs.
- Improved User Experience: Provides consistent connectivity and service quality across WiFi and LTE.
- Security: Protects user data on untrusted WiFi networks.
- Enhanced Indoor Coverage: Improves connectivity in areas where cellular signals are weak or unavailable.
- QoS (Quality of Service): Ensures that VoWiFi and other critical services maintain high-quality performance.
