There are different Open vRAN deployment models, bring clear flexibility and adaptability to networks, so that different use case requirements can be addressed dynamically and provide a more efficient and rapid response to business requirements.
The 3GPP model for 5G architecture relying on Open interfaces together with RAN virtualization, allows an optimized deployment of DU/CU, bringing more flexible solutions to address different business demands that would be extremely difficult to meet with traditional RAN deployment architectures:
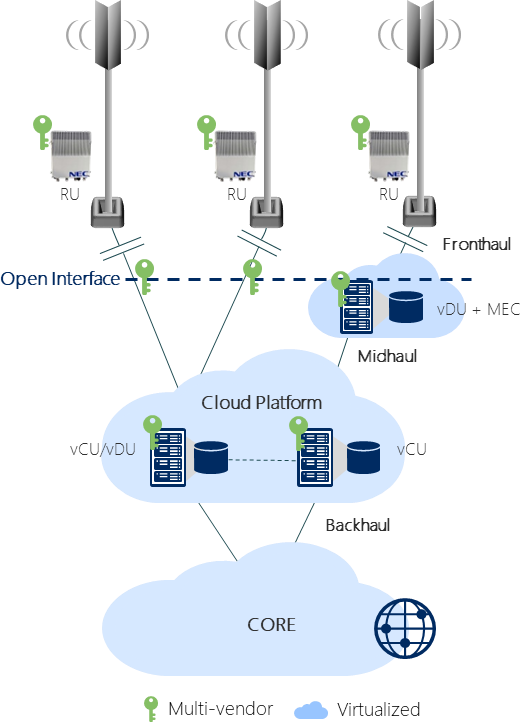
- RU, vCU, and vDU are collocated – a typical “Network-in-a-box” deployment, addressing specific enterprise needs (office, stadiums, etc);
- RU separated and vCU/DU collocated – Open Fronthaul(ORAN Option 2x);
- RU and vDU collocated, vCU separated – for latency-sensitive radio CU centralized allows a more flexible scaling of resources (3GPP option 2 F1);
- RU separated and distributed vDU, vCU separated – typically vDU can be deployed jointly with edge computing resources depending on operator preferences;
One of the major advantages of Open vRAN is the ability to choose multiple vendors for different parts of the solution, and the ease to swap vendors as needed.
Whilst open interfaces are critical, this goal can only be achieved through orchestration. With the baseband unit further disaggregated and the majority of the solution virtualized compared with previous architectures, it is simply no longer possible to rely on legacy operations to manage the dynamic nature of resources and services. The entire process must be automated.
Source: NEC
