To support the Multi-Vendor connectivity, 3GPP studied the “CU-DU Split” Function, So What is CU and DU?
Centralized RAN architectures have a baseband unit (BBU) that handles all baseband processing and is connected to the mobile core over a backhaul network, and to multiple remote radio heads (RRH) through CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface) links.
In a 5G cloud RAN architecture the BBU functionality is split into two functional units; a Centralized Unit (CU) and a Distributed Unit (DU).
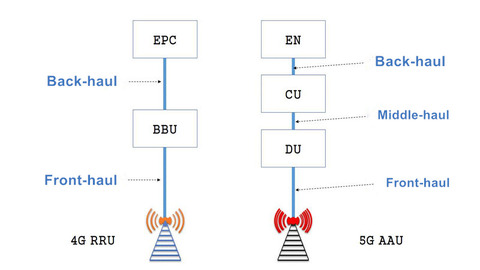
There’re different types of transmission networks used for the frontal, The front-haul interface is between the aggregated node and distributed node and here in 5G NR, 3GPP defined the aggregating node as the CU and the distributed nodes as DU and is called CU-DU Interface.
The CU-DU Interface Configurations
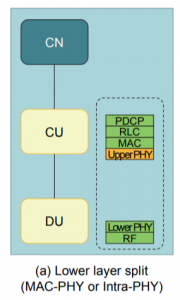
a) Lower-Layer Split
A functional split between the MAC and PHY layer or withing the PHY layer itself can improve radio performance through advanced inter-cell coordination including the MAC scheduler. The transmission network used here for the front-haul would satisfy high requirements for latency.
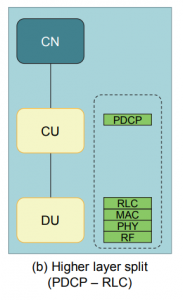
b) Higer-Layer Split
Here the functional split between the Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) layer and Radio Link Control (RLC) layer and an interface between the CU and DU with that functional Split as an F1-Interface. This enables the aggregation benefits of C-RAN to be enjoyed while reducing the required front-haul transmission BW.