Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is a technology that enables the network owner to analyze internet traffic through the network in real-time and differentiate it according to its payload. Since this has to be done in real-time at high speeds, it cannot be implemented by software running on normal processors or switches.
Originally the Internet protocols required the network routers to scan only the header of an Internet Protocol (IP) packet. The packet header contains the origin and destination address and other information relevant to moving the packet across the network. The “payload” or content of the packet, which includes (all or part of) the text, images, files, or applications transmitted by the user, was not considered to be a concern of the network operator. DPI allows network operators to scan the payload of IP packets as well as the header.
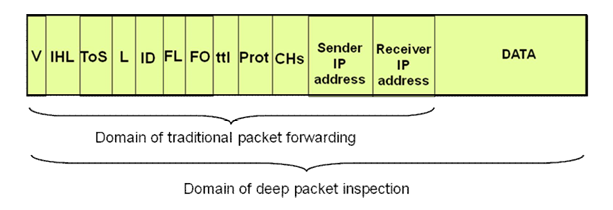
DPI devices have the potential to look inside all traffic from a specific IP address, pick out the HTTP traffic, then drill even further down to capture traffic headed to and from a specific mail server, and can then reassemble e-mails as they are typed out by the user. DPI devices are designed to determine what programs generate packets, in real-time, for hundreds of thousands of transactions each second.
Conclusion
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a method of examining the content of data packets as they pass by a checkpoint on the network. With normal types of stateful packet inspection, the device only checks the information in the packet’s header, like the destination Internet Protocol (IP) address, source IP address, and port number. DPI examines a larger range of metadata and data connected with each packet the device interfaces with.
In this DPI meaning, the inspection process includes examining both the header and the data the packet is carrying.
