Both Open RAN and vRAN offer a significant benefit by separating RAN hardware from software. Consequently, software for the virtualized Centralized Units and Distributed Units (vCU/DUs) can run on any Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) hardware. This support for commodity hardware enables operators to reduce capital costs by taking advantage of the economies of scale afforded by COTS and web-scale General Purpose Processors (GPP).
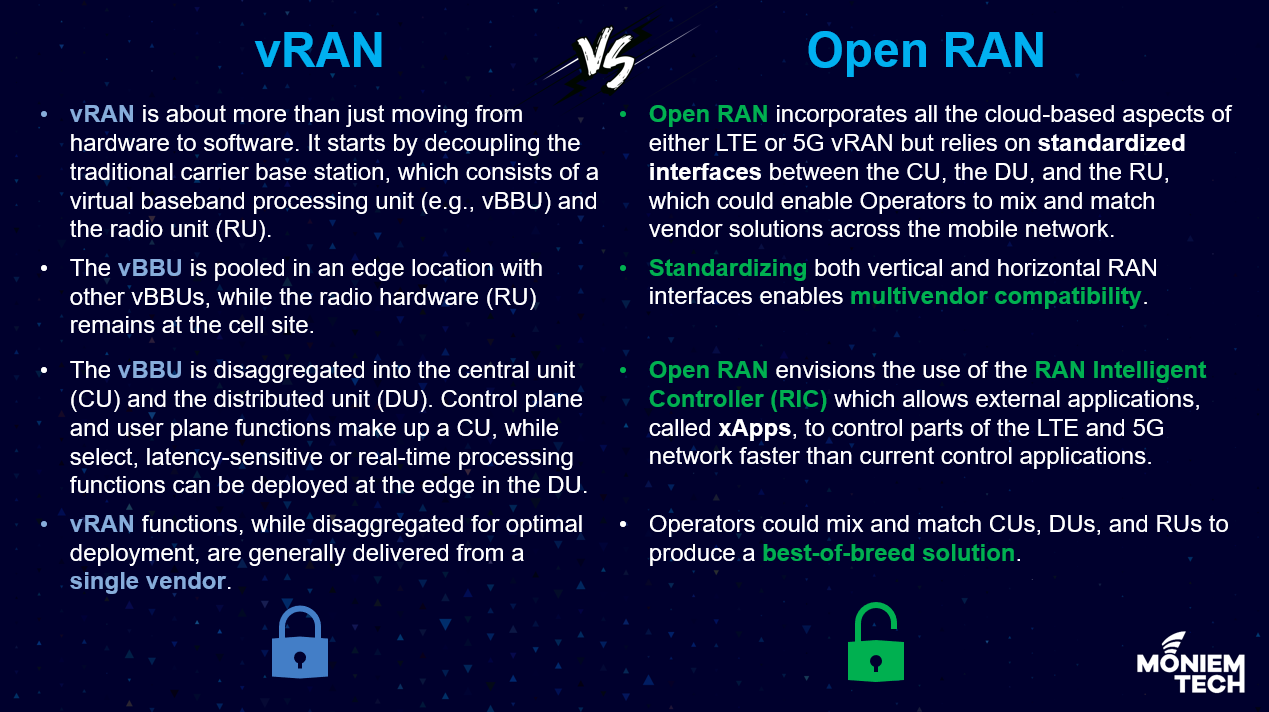
The primary drawback of vRAN is that it uses proprietary interfaces between radios and other network elements, thereby locking the operator into a single RAN vendor.
Open RAN opens the software interfaces to other network elements, giving the operator the freedom to combine RAN gear from multiple vendors. For example, the best vDU/CU software solution may be different than the best radio hardware.
