The EPC is continuous from the GPRS, which is used for mobile data services.
GPRS was first a packet switched (PS) mobile data service introduced in 3GPP release 97.
The main difference between PS data service and CS data service is that PS data service does not have a constant resource reservation and the usage is volume-based rather than time-based.
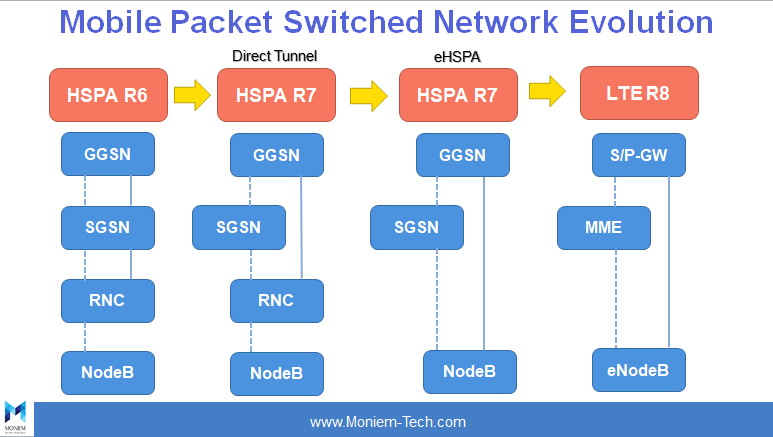
In GPRS there is a dedicated core for PS data service; the PS core that consists of SGSN and GGSN providing ‘always on’ IP-based connectivity to data services.The first GPRS release was improved with higher data rates in 3GPP Release 98, and the first universal mobile telephone system (UMTS) release was introduced in 3GPP Release 99.
In Release 99 UMTS network there came new access technology and a new interface from the PS core to the radio access network (RAN).
The next 3GPP releases introduced higher bit rates and network optimizations like Direct Tunnel in 3GPP Release 7.
In 3GPP Release 8 whole system was re-designed under the system architecture evolution (SAE) work item.
One difference between the GPRS core and EPC is the strict and in-built separation of control and user plane in EPC. This is possible in GPRS as well by using the direct tunnel feature, but with direct tunnel the SGSN user plane is used, for example, in an international roaming scenario.
For LTE the EPC contains two functional elements in the user plane, the S-GW and P-GW, and one element in the control plane, the MME. As a consequence, a minimum of two functional elements (eNodeB, combined S-GW/P-GW) are in the EPS user plane path, which means a higher degree of simplicity and less latency.