First, We start with 1G and 2G where the baseband unit was co-located with Radio unit and in this approach which was the “Traditional Network”, we can see the antenna in the top of the tower is connected to the site [Baseband & Radio unit] by very thick cables (Coax-Cables).
In this approach, the Baseband processing is located in a large container with air conditioners, colling, power sources and different physical alarms.
Moving to today’s networks,3G and 4G networks which they follow another advanced approach is called “Distributed Network“, where the Radio unit is splitted than the baseband unit. Radio Unit is now on the top of the tower while the baseband unit is still at the bottom of the tower.
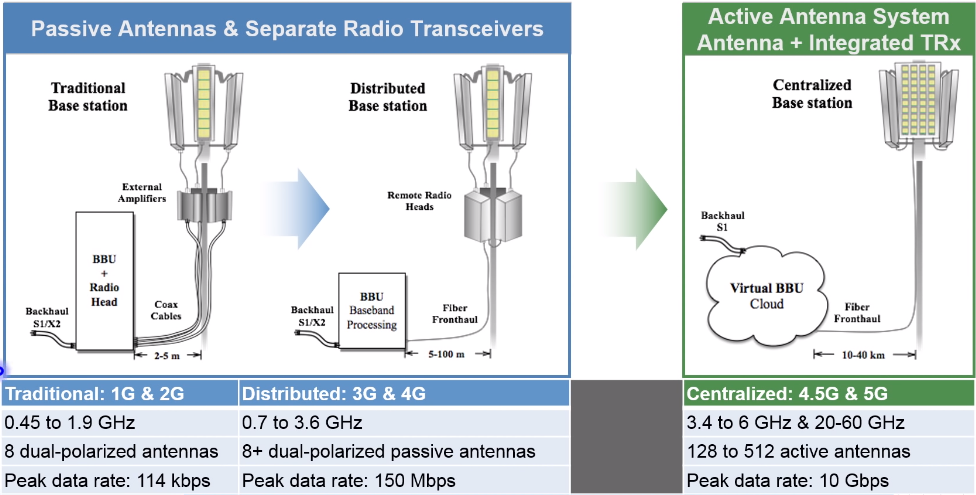
But the question now is: How Distributed Network is more effective than the Traditional Network?
Replacing the lossy high power cables with a fiber front-haul and this will increase the power gain.
Towards to 4.5G and 5G, Introducing Active Antenna System (AAS) [ Radio Unit + Antenna System ] and centralized BBU that can be located in a remote DC (Data Center) and this is called C-RAN or Centralized RAN, this will reduce the CAPEX, less power consumption and a fast deployment roll-out.
