Network virtualization leads the way for 5G to meet high flexibility and agility expectations.
It allows running complex network functions (namely, Virtual Network Function – VNF) on top of a virtualized infrastructure, hosted at central or edge telco cloud.
It allows running complex network functions (namely, Virtual Network Function – VNF) on top of a virtualized infrastructure, hosted at central or edge telco cloud.
One big advantage of using VNF, is the possibility of dynamically scaling, depending on traffic load (i.e. instantiate new resources to VNF when the traffic load increases, and reduce the number of resources when
the traffic load decreases).
5G will mainly rely on Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software Defined Network (SDN) to build flexible and on-demand instances of functional networking entities, via Virtual Network Functions (VNF).
5G core Network Architecture
The 5G core network architecture has been devised with the aims:
(i) to keep compliance with the concept of 3GPP communication reference interfaces (point-to-point).
(i) to keep compliance with the concept of 3GPP communication reference interfaces (point-to-point).
(ii) to evolve in near future to a service-oriented architecture, where the 5G core control network functions communicate via a common bus, through the concept of producers and consumers.
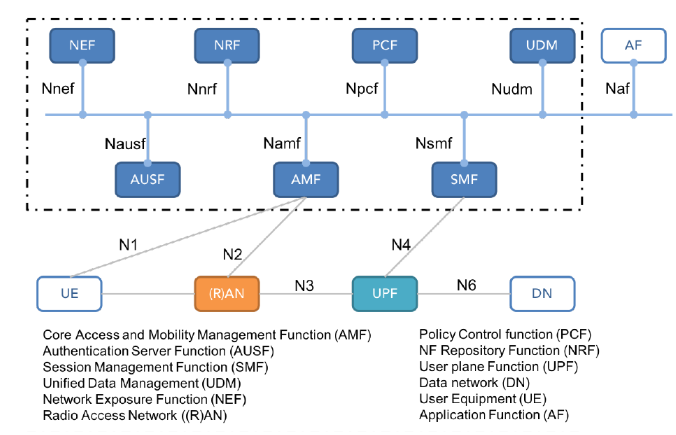
Regarding the 5G core functions, some are similar to 4G EPC ones and some are completely newly designed.
Notably, the access control and session management functions are combined in the Mobility Management Element
(MME) of EPC, but separated in 5G core to better support fixed access and ensure scalability and flexibility.
So Simplifying core network architecture to implement on demand configuration of network functions through
control and user plane separation, component-based functions, and unified database management is very important step towards 5G.
control and user plane separation, component-based functions, and unified database management is very important step towards 5G.
