Introduction
5G is the future network revolution of mobile technology. The characteristics and usability are exceeding human expectations. With its extra high speed, it owns the prospects to change the face of cell phone usability.
5G will improve the mobile network that it will interconnect people, machines, objects, and devices and gain control over many fields. It will reach top levels of performance and efficiency that will upgrade the new user experiences and create connections between new industries. 5G will reach multi-Gbps peak rates, massive capacity, ultra-low latency, and overall better user experience.
The 5G network will support many commercial services (e.g., medical) and regional or national regulatory services (e.g., MPS, Emergency, Public Safety) with requirements for priority treatment. Some of these services have common QoS qualities like latency and packet loss rate but may have other priority needs.
For instance, UAV control and air traffic control may have great latency and reliability requirements; however, it may not have the same priority needs. Moreover, voice-based services for MPS and Emergency share the same QoS as used for normal public voice communications, but may also have different priority requirements. The 5G network will need to support mechanisms that enable the decoupling of the priority of a particular communication from the associated QoS characteristics. For example, reliability and latency to allow flexibility to support several priority services (that need configuration which meet operator’s requirements and are at the same time consistent with operator’s policies and corresponding national and regional regulatory policies).
The network needs to support flexible means to make priority decisions based on the state of the network (e.g., during disaster events and network congestion) recognizing that the priority needs may change during a crisis. The priority of any service may need to be different for a user of that service based on operational needs and regional or national regulations. Therefore, the 5G system should allow a flexible means to prioritise and enforce prioritisation among the services (e.g., MPS, Emergency, medical, Public Safety) and among the users of these services. The traffic prioritisation may be enforced by adjusting resource utilization or pre-empting lower priority traffic.
The network must offer a means to provide the required QoS (e.g., reliability, latency, and bandwidth) for a service and the ability to prioritize resources when necessary to meet the service requirements. The already-existing QoS and policy frameworks manage latency and enhance reliability by traffic engineering. In order to support 5G service requirements, it is necessary for the 5G network to offer QoS and policy control for reliable communication with latency required for a service and enable the resource adaptations as necessary.
The potential 5G requirements contain more than 70 different use cases categorized into different groups:
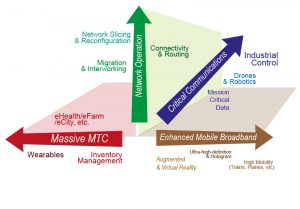
1-Massive Internet of Things
Massive Internet of Things covers mainly use cases with a huge number of devices (for example, sensors and wearables). This group of use cases is especially related to the new vertical services, like smart home and city, smart utilities, e-Health, and smart wearables, etc.
2-Critical Communications
The main scopes where upgrades are necessary for Critical Communications are latency, reliability, and availability to enable, for instance, tactile Internet and industrial control applications.
3-Enhanced Mobile Broadband
Enhanced Mobile Broadband has a variety of use case families relevant to higher data rates, density and user mobility, deployment and coverage, devices with different user data rates, fixed mobile convergence, and small-cell deployments.
4-Network Operation
The use case group Network Operation manages the functional system needs, including features like new value creation, security, capabilities, optimizations, and improvements, etc.
Requirements:
- The 5G system shall allow flexible mechanisms to establish and enforce priority policies among the different services (e.g., MPS, Emergency, medical, Public Safety) and users.
- The 5G system shall be able to provide the required QoS (e.g., reliability, latency, and bandwidth) for a service and support prioritization of resources when necessary for that service.
- The 5G system shall allow decoupling of the priority of a particular communication from the associated QoS characteristics such as latency and reliability.
- The 5G system shall be able to support a harmonised QoS and policy framework applicable to multiple accesses.
- The 5G system shall be able to support E2E (e.g., UE to UE) QoS for a service.
- The 5G system shall be able to support QoS for applications in a Service Hosting Environment.
Summary:
The number of use cases for a next generation mobile network will increase rapidly and the possibilities will need much more different requirements on the system. In this White Paper, we have outlined the use cases and requirements for 5G but also the key design principles – flexibility and reliability.
The future may seem far ahead but the phase for defining the requirements is now and what’s more, any new technology or system that we design for 5G has to be soundproof and remain till 2030 at least.
5G will come and even though we are still in an exploratory phase, Nokia is already setting out what 5G will deliver and how it will deliver it.
Sources:
- 3GPP TSG-SA WG1
- 5G Use Cases and Requirements White Paper
