As per the Ericsson Mobility Report, November 2019, by the end of 2025, we expect 5G to have 2.6 billion subscriptions covering up to 65 percent of the world’s population and generating 45 percent of the world’s total mobile data traffic, making it the fastest developing mobile communication technology to have ever been rolled out on a global scale. So MNO started to think in a different solutions to can solve the upcoming capacity issue.

As the Radio Access Network (RAN), which is the most expensive part of the mobile network in terms of CAPEX and OPEX and the source of 80% of performance problems that affect the customer experience, So it’s the main of focus for Mobile Network Operators.
4G technology is more efficient than previous generations in handling high-bandwidth traffic, but the conventional RAN architecture widely deployed today is challenged to deliver the additional capacity, cost savings, service agility, and scalability that CSPs need to meet future demand.
Some Facts:
- eNodeB comprises a baseband unit (BBU) and remote radio units (RRUs).
- The BBU and RRU are typically located at the base of the cell tower or in a nearby cabinet, and the RRU is connected to the antennas at the top of the tower via coaxial cable.
- In a split architecture, the RRU is located at the top of the cell tower with the antennas; it connects to the BBU via fiber using the Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) protocol to transport the digitized radio frequency data.
Virtual RAN (vRAN)
In the vRAN model, the BBUs are virtualized. The vBBUs are deployed on multiple NFV platforms on industry-standard x86 hardware and consolidated in centralized data centers, while remote radio heads (RRHs) are left at the cell sites at the edge of the network.
vRAN leverages standard server hardware that cost-effectively scales up or down processing, memory, and I/O resources with demand and infuses the RAN with capacity for application intelligence to significantly improve service quality and reliability.
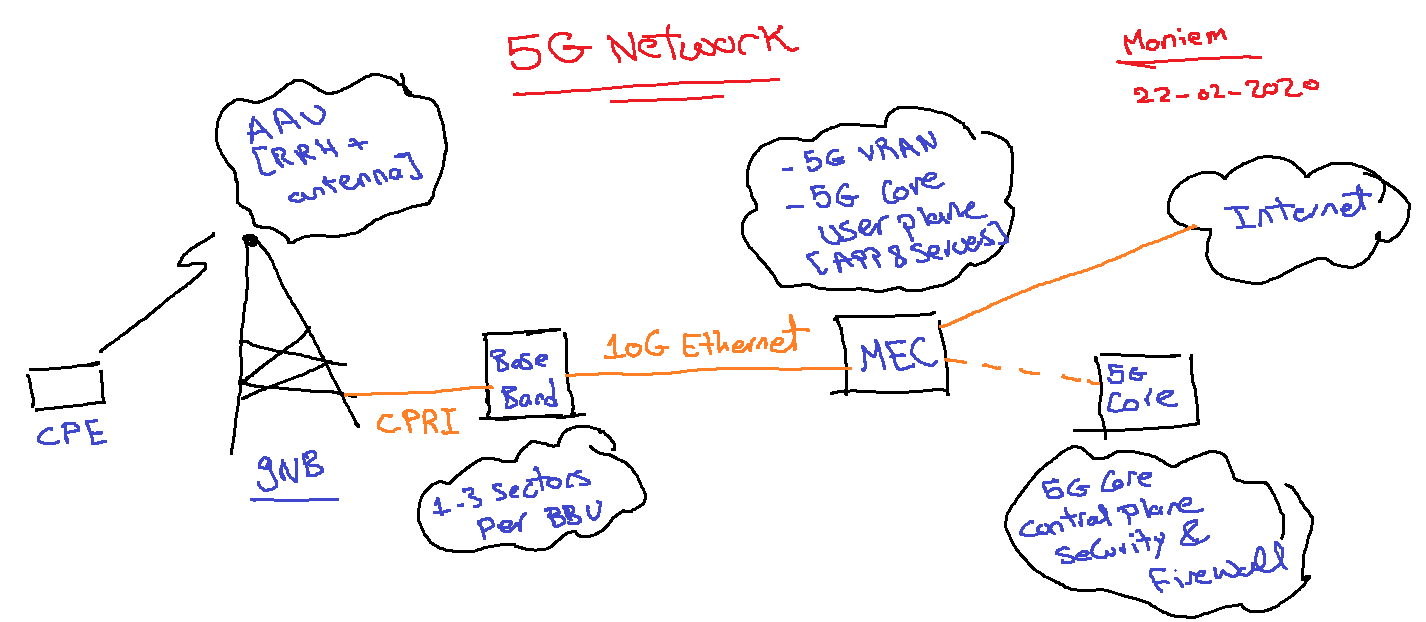
Depending on how the eNodeB functions are split, the architecture also allows for Ethernet and IP fronthaul transport, which gives services providers more cost-effective options for fronthaul transport.
Conclusion
By extending the benefits of NFV from the core network to the RAN, virtualized RAN is the optimal solution for cost-efficiently increasing capacity, reducing costs, and creating new services.
For more details: 5G Overview Training & 5G RAN Training
Source
- Ericsson.
- Altiostar.
- Mavienar.
- Wind
