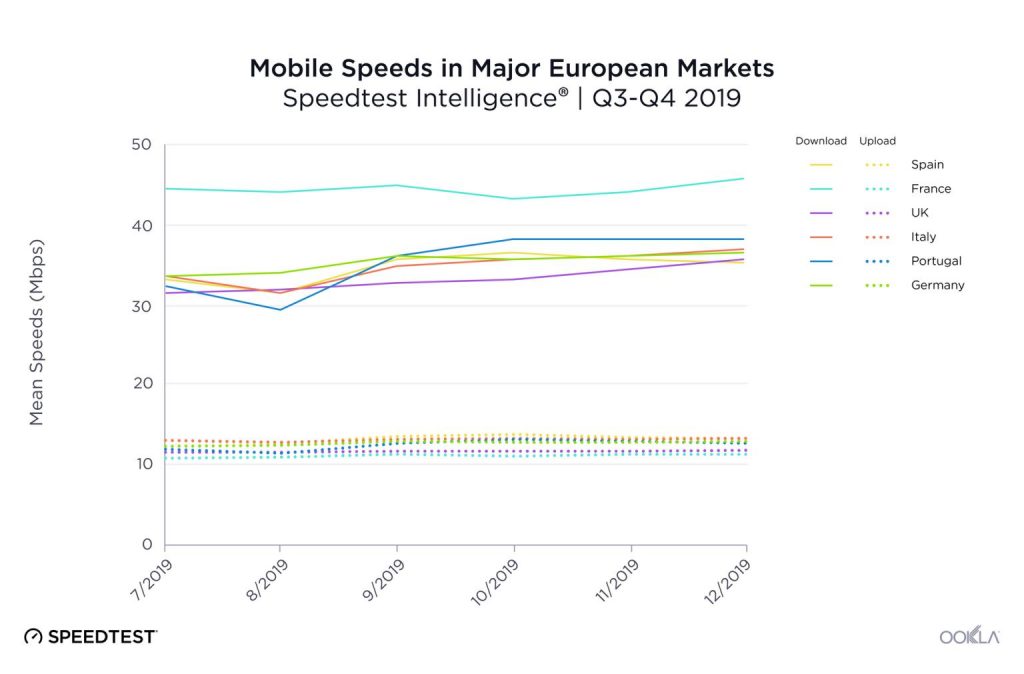
Interesting Figure from OoKla about the Mobile Speeds in Europe
– France ranks the First for mobile download speed.
– Spain showed the fastest mean upload speeds on mobile at 13.12 Mbps during Q3-Q4 2019.
Rakuten Mobile Rocks!
When Rakuten will launch 8th April, it will be with one plan only, UN-LIMIT, priced at 2980 JPY (25 EUR).
First year will even be free. This is valid for the first 3 million subscribers.
The data volume is unlimited when the customers are on Rakuten’s own network – when roaming into KDDI’s network, the bucket is just 2 GB per month.
Rakuten is also avoiding negative lock-in such as SIM lock, binding contracts and contract cancellation fees.
Also Rakuten invest with AST, US satellite start-up to deliver 4G and 5G mobile broadband services from space to fill coverage gaps.

GSA Latest Report
– 63 operators in 35 countries have launched one or more 3GPP compliant 5G services (including 55 mobile and 34 FWA services).
– 359 operators are investing in 5G networks in the form of tests, trials, pilots, planned and actual deployments.
– 69 operators investing in LTE-M; 45 have launched the technology in their network.
– 239 operators hold licences to use spectrum for TD-LTE services, 169 of which are known to be actively using the spectrum.
– 366 operators investing in either LTE-Advanced or LTE-Advanced Pro technologies. Of those, 325 operators have deployed/launched LTE-Advanced or LTE-Advanced Pro technologies in their commercial networks.
5G Core (5GC) Is
1. Cloud Native Virtual Network Functions
=> Cloud native means “containerized micro-services deployed on bare metal and managed by Kubernetes”.
2. Service-based Architecture
=> 5G introduced many network functions (NFs) operating on the strong virtualization and cloud-ready software like Mobility Management Function (AMF), Session Management Function (SMF), User Plane Function (UPF), Policy Control Function (PCF), Unified Data Management (UDM), and Network Repository Function (NRF).
Operators can combine these network functions to deliver customized service or service packages to their customers. They can also be upgraded individually, which makes it possible for operators to deploy new software more quickly. With these network functions, operators can also use 5G Core to support 3G or 4G services.
3. Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS)
=> Operators can deploy user plane functions closer to the radio access network, to support low latency services, while deploying a 5 G core with control plane functions in the core data center.
Source: Telecoms
Studying 5G RAN or 5G NR (New Radio)
I prepared some of the useful topics you can start with to be ready for digging in-depth in the 5G RAN domain.
Just follow this Hashtag TelecomBasics, I will update all needed topics as a prerequisite to read about 5G.
How IMS Works with the 5G Core?
Despite the focus on the headline abilities of 5G such as ultra-low latency and support for network slicing, Voice will remain a vital service that Mobile Network Operator (MNO) will continue offering with the new networks.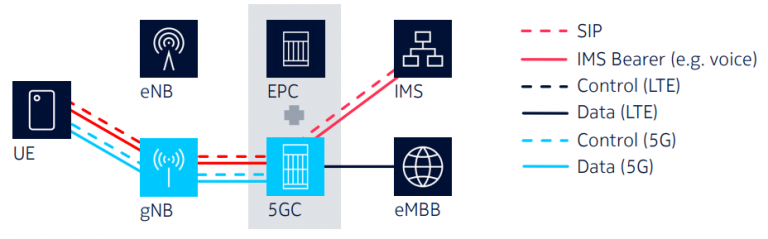 Useful Terms and Abbreviations in 5G Domain
Useful Terms and Abbreviations in 5G Domain
5GC: 5G Core
5GS: 5G System
AMF: Access and Mobility Management Function
SMF: Session Management Function
SPR: Subscription Profile Repository
UDM: Unified Data Management
UDR: User Data Repository
PCF: Policy Control Function
UPF: User Plane Function
gNB: NR Node B
NG-RAN: Next-Generation RAN
NR: New Radio
SA: Standalone
NSA: Non-Standalone
CP: Control Plane
UP: User Plane
CUPS: Control Plane User Plane Separation
EPC: Evolved Packet Core
EPS: Evolved Packet System
EUTRAN: Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access NW
IMS: IP Multimedia Subsystem
MBB: Mobile Broadband
MME: Mobility Management Entity
NAS: Non-Access Stratum
PCRF: Policy Control and Charging Rules Function
PDN: Packet Data Network
PDU: Protocol Data Unit
PGW: Packet Data Network Gateway
SGW: Serving Gateway
UE: User Equipment
Ooredoo Qatar Deploys Ericsson Spectrum Sharing
Ericsson and Ooredoo Qatar have accomplished a major milestone in a network modernization project by completing the upgrade of more than 2,400 sites across Qatar, enhancing the capabilities of Ooredoo’s network.
As part of this network modernization, Ooredoo has deployed Ericsson Spectrum Sharing sites on its commercial network in Doha to facilitate an efficient, flexible and smooth evolution towards nationwide 5G coverage.
5G New Radio Release 16 Enhancement
5G Release 16 near to be closed next June 2020.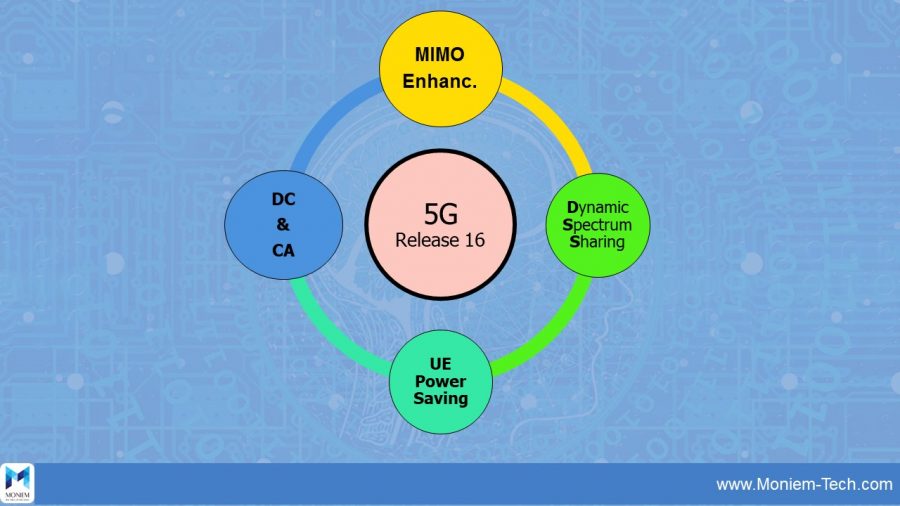
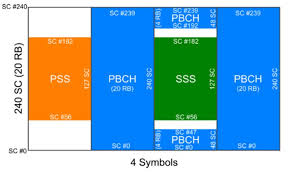
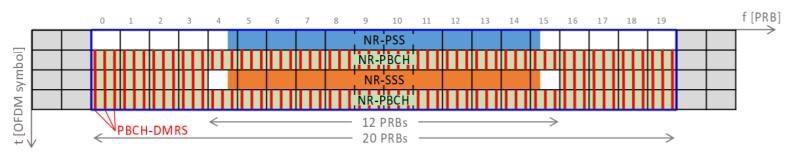
SS/PBCH Block in 5G NR
– The UEs synchronize to the Network by “listening” to the Primary and Secondary Synchronization Signals (PSS and SSS).
– The vertical separations are the Resource Blocks (RB) or a group of 12 subcarriers.
– The horizontal separations are the OFDM symbols, 4 OFDM symbols together with 20 RBs form a so-called “SS/PBCH (Synchronization Signals/ Physical Broadcast Channel) block”.
– The PSS and NSS are transmitted over 127 subcarriers, i.e. about 10.5 RBs. (They are designed to carry the Physical Cell ID (PCID) selected from 1008 candidates.).
– Once synchronized with the PSS and NSS, the UEs can retrieve the full SS/PBCH structure, and thus “listen” to the Physical Broadcast Channel (PBCH) and its associated Demodulation reference signals (DM-RS).
– The PBCH carries only the minimum system information necessary for initial access, such as system frame number (SFN), initial configurations for PDCCH, PDSCH and DM-RS, and information required to determine the frame timing such as SS/PBCH block index and half-frame index. These are referred to as “System Information Block 1 (SIB1)”.
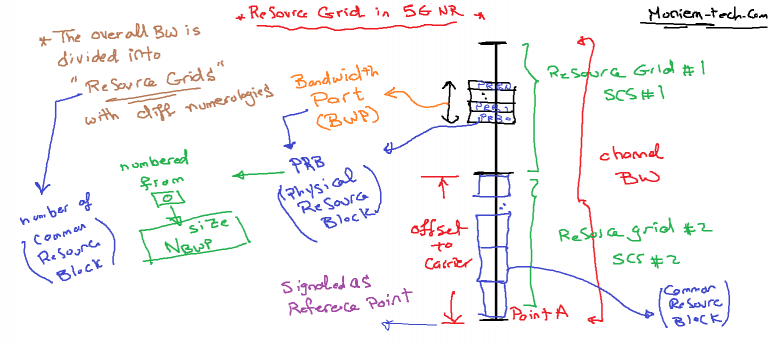
What Is the “Point A” Concept in 5G NR?
I know that Resource Grid in 5G is different and more complicated than 4G, and 5G NR introduced a new concept is called Point A. So What is Point A?
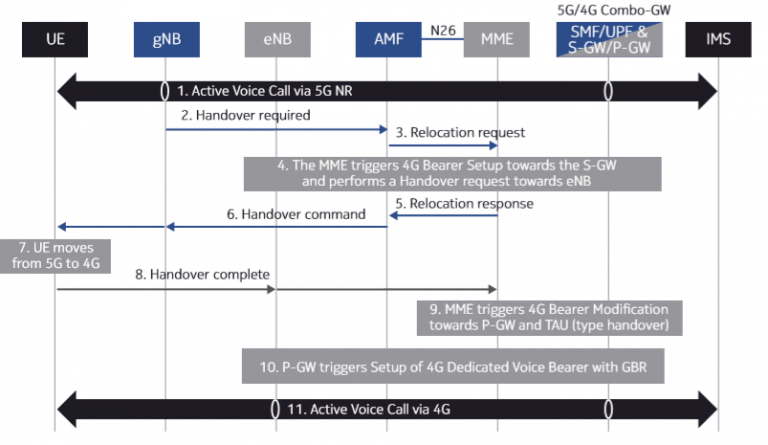
How Does 5G Do Voice Handover to 4G?
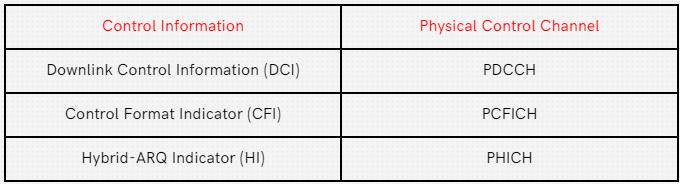
Are there PHICH and PCFICH in 5G NR?
Why Are SSB Measurements Essential in 5G NR?
Why we need SSB in 5G?
Why we don’t use the 4G concept of sending SS signals and PBCH all the time?
Why the frequency of sending SS signals and PBCH is changed to be equal in 5G Versus 4G?
Did You Know!
In LTE the synchronization signals are transmitted by using omnidirectional antennas (beam-forming, if employed, applies only after synchronization, i.e., during the data transmission).
In 5G NR gNB employs beam sweeping already when broadcasting the synchronization signals. Hence, initial access for mmWave NR becomes much more challenging, since both the UE and the gNB have to detect the correct directions and align the beams before subsequent data transmission.
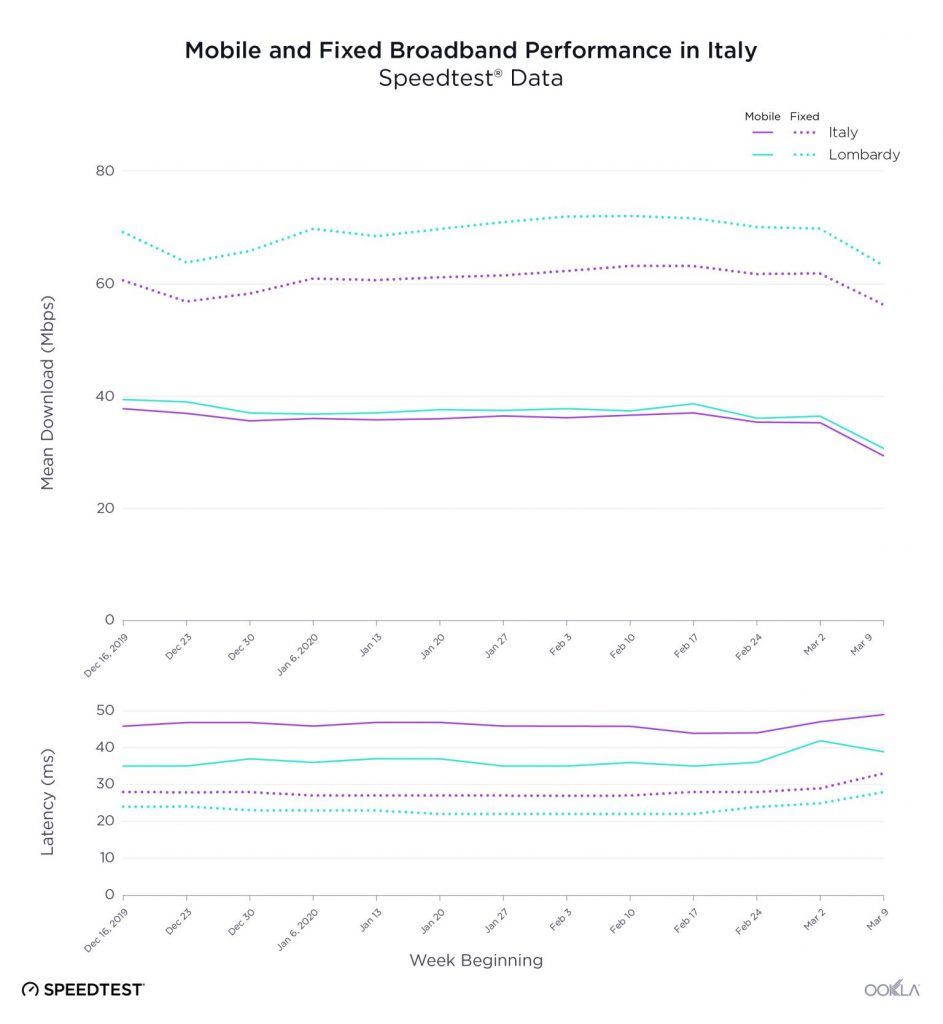
COVID-19’S Impact on Global Internet Performance
This is interesting figure from Ookla that explains the COVID-19’s impact on Italy.
In Italy, Ookla reported that it didn’t see much in terms of major changes to network speed or latency until the week of February 17, when speeds began to decrease slightly in Italy as a whole and in the Lombardy region, which has been the heart of the Italian outbreak. Then, from March 2-9, speeds took a sharper downward trajectory.
Is there a Relation between 5G and COVID-19?
As I received many questions on this topic and read different fake news, I wrote this article.
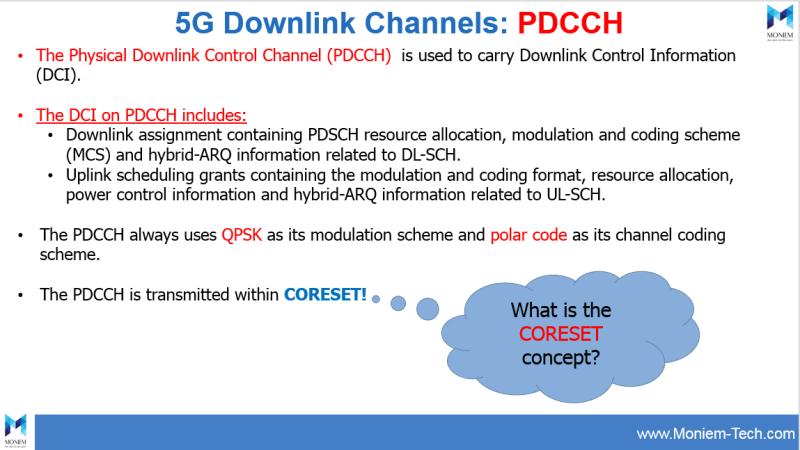
5G Downlink Channels
One of the most important topics in 5G New Radio (NR) is CORESET or Control Resource Set (CORESET).
A Control Resource Set (CORESET) is defined as a set of physical resources(i.e, a specific area on NR Downlink Resource Grid) and a set of parameters that are used to carry PDCCH/DCI.
Frequency Domain
In 5G NR, can be set in any value in the multiples of 6 RBs.
Time Domain
In 5G NR, defined by RRC parameter ControlResourceSet.duration.
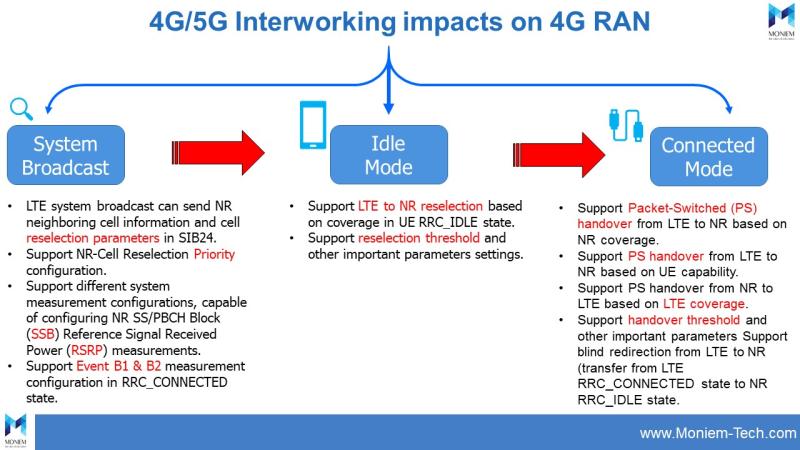
How Can 5G Impact 4G from RAN Perspective?
If 5G option 2 is deployed, the impact on 4G RAN will be as below:
1] System Broadcast and measurement.
2] Idle mode operation.
3] Connected mode operation.
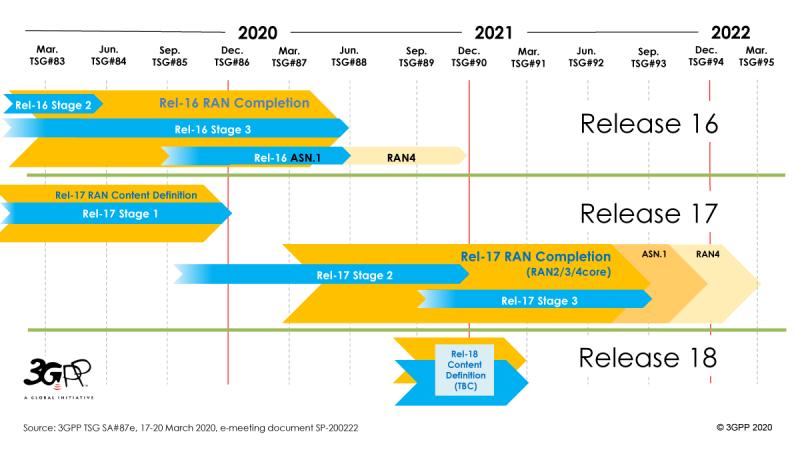
Rel-16 Stage 3 Freeze Now June 2020 (Shifted by 3 Months)
 3GPP Defines gNB Functionality
3GPP Defines gNB Functionality
What is gNB?
A logical NG-RAN node providing NR user plane and control plane protocol terminations towards the UE, gNB is divided into following logical entities:
What is gNB-CU (CU – Central Unit)?
• A logical node hosting RRC, SDAP and PDCP protocols, and which controls the operation of one or more gNB-DUs
• The gNB-CU also terminates F1 interface connected with the gNB-DU.
What is gNB-DU (DU – Distributed Unit)?
• A logical node hosting RLC, MAC and PHY layers, and its operation, that is partly controlled by gNB-CU.
• One gNB-DU supports one or multiple cells. One cell is supported by only one gNB-DU.
• The gNB-DU terminates F1 interface connected with the gNB-CU.
F1: 3GPP based interface for gNB-DU<->gNB-CU connection.
NG RAN: Next Generation Radio Access Network
NR: New Radio
Source: 3GPP TS 38.300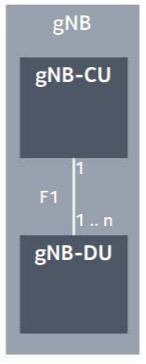
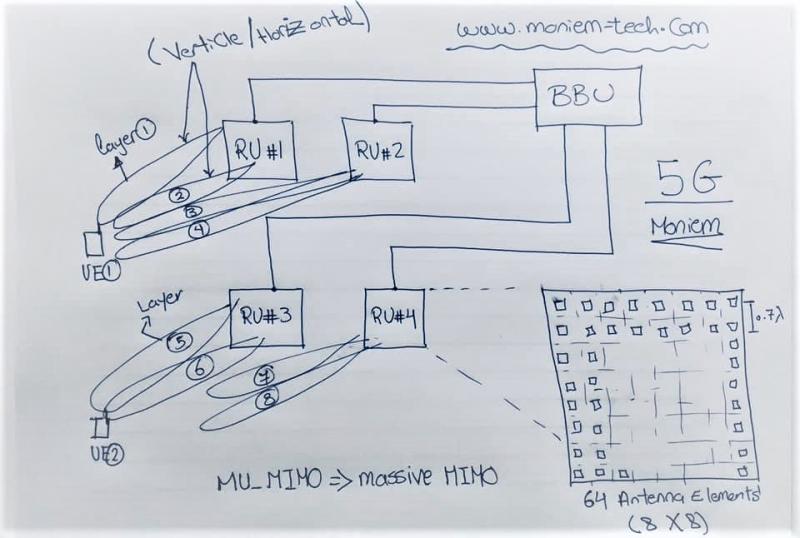
Multi-User MIMO or “MU-MIMO”
It allows messages for different users to travel securely along the same data pipelines, then be sorted to individual users when the data arrives at their mobile devices.
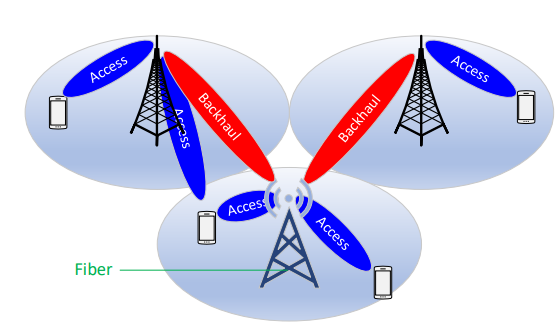
What Is IAB in 5G NR?
IAB: It stands for Integrated Access and Backhaul, It supports wireless backhaul and relay links in-band or out-of-band with access links. Significant 5G NR bandwidth can be split between access and backhaul links, especially in mmWaves.
5G New Radio Is Different from 4G Physical Layer
= Always-on transmitted signals.
= News Physical Signals in DL and UL.
= No CRS anymore, So no one size fits all concept.