One of the main challenges of successful 5G deployments is network densification.
This challenge derives from the need for additional Capacity everywhere and from the use of higher frequency bands in the radio access network (RAN).
There are two main approaches to densifying the RAN – Centralized RAN and Decentralized RAN.
- The decentralized approach follows the classic network architecture and creates a fully functional small cell.
- The centralized RAN approach splits the base station (eNB or gNB) functionality and allows operators to deploy simple, cost-efficient remote radio heads (4G RRHs) or radio units (5G RUs) in remote sites while keeping baseband processing functionality in a more central location.
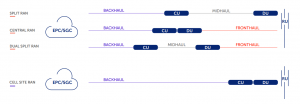
There is a major tradeoff, though, between these two methods. While #centralized RAN brings significant benefits with regards to the cell site cost and the level of coordination of adjacent cells, the #decentralized RAN architecture requires a significantly lower-capacity connection to each site.
Source: Ceragon
