Bandwidth Parts & Bandwidth Adaptation Basic Concepts
As per the definition in TS38.300, with Bandwidth Adaptation (BA), the receive and transmit bandwidth of a UE need not be as large as the bandwidth of the cell and can be adjusted: the width can be ordered to change, e.g. to shrink during the period of low activity to save power; the location can be ordered to change, e.g. to allow different services.
A subset of the total cell bandwidth of a cell is referred to as a Bandwidth Part (BWP), and BA is achieved by configuring the UE with BWP(s) telling the UE which of the configured BWPs is currently the active one.
3GPP TS 38.211 specifies Bandwidth Parts (BWP) as a contiguous set of physical resource blocks, selected from a contiguous subset of the common resource blocks for given numerology (µ) on a given carrier. And for a single UE configuration, the following rules apply.
- A UE can be configured with up to four bandwidth parts in the downlink, with a single downlink bandwidth part being active at one time.
The UE is not expected to receive PDSCH (Physical Downlink Data Channel), PDCCH, or CSI-RS (Channel State Information Reference Signal) outside an active bandwidth part. - The same maximum four bandwidth parts can be configured for a UE in the uplink with a single uplink bandwidth part being active at once.
- If a UE is configured with a supplementary uplink (SUL), it can additionally be configured with up to four bandwidth parts in the supplementary uplink, with a single supplementary uplink bandwidth part being active at a given time.
The UE shall not transmit PUSCH or PUCCH (Uplink Data and Control Channels) outside an active bandwidth part. For an active cell, the UE shall not transmit SRS (Sounding Reference Signal) outside an active bandwidth part. - There are, however, exceptions as the UE may need to perform Radio Resource Management (RRM) measurements on the downlink or transmit SRS in the uplink, outside of its active BWP. This is therefore done via measurement gap.
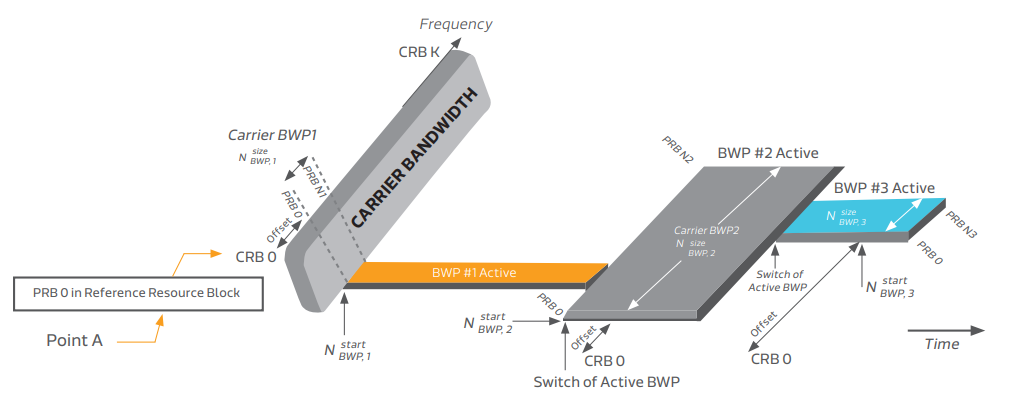
By definition, Carrier Resource Block (CRB) provides the RB numbering throughout the overall carrier bandwidth from CRB0 to CRB_Max (for example CRB272 in case of 100 MHz in FR1 carrier), while Physical Resource Block (PRB) provides the RB numbering within each BWP.
Point A is a common reference point for resource block grids and is obtained by higher layer parameters – either offsetToPointA or absoluteFrequencyPointA according to 3GPP TS 38.211, and is used as the reference to apply frequency offsets that are signaled by the network to identify the lowest subcarrier of the lowest RB for a designated BWP.
Bandwidth Parts Allocations
Taking the BWP definition, and the fact that up to four BWP could be configured for a UE, different BWP allocation scenarios are possible and each could better serve certain use cases.
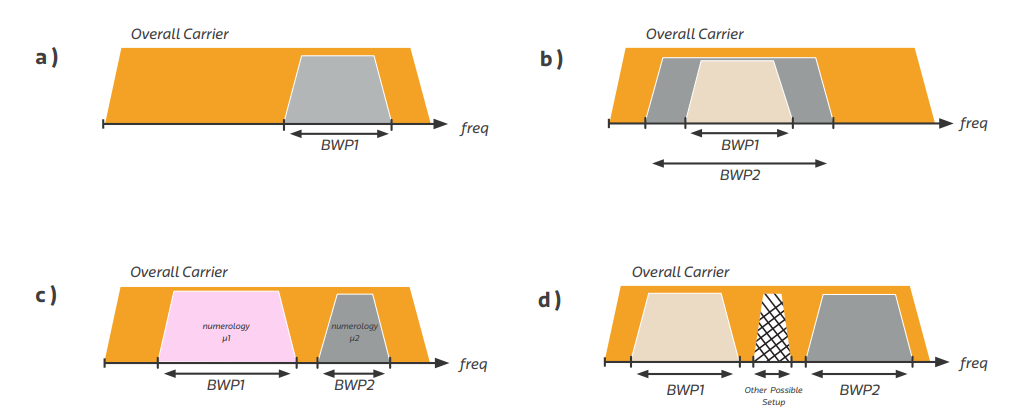
- Allocation (a): Supporting reduced UE bandwidth capability is especially helpful for devices with limited RF capability or those not capable of full carrier bandwidth.
- Allocation (b): Supporting reduced UE power consumption for intermittent and bursty traffic profiles.
- Allocation (c): Supporting two non-contiguous BWP with different numerologies allowing different services multiplexing.
- Allocation (d): Supporting the non-contiguous spectrum, allowing services to be allocated between different BWPs. This is not yet part of Release 15 and could be added to future releases.
Source: MediaTek
