The evolution of 5G New Radio (NR) has progressed swiftly since the 3GPP standardized the first NR release (release 15) in mid-2018. Not only is release 16 nearly finalized but the scope of release 17 has also recently been approved.
3GPP plans to evolve 5G in three phases:
- Phase 1 – 3GPP Release 15 provided a new radio access network (RAN) and a new core network built on a service based-architecture to meet the highthroughput mandate leveraging automation and cloud techniques.
- Phase 2 – 3GPP Release 16 extended capabilities in the RAN and core to drive down latency to support real-time sensitive services, providing support for more bands of spectrum.
- Phase 3 – 3GPP Release 17 will define more frequency ranges and implementation of non-terrestrial/satellite networks, as well as an architecture called NR-Light that reduces network complexities to meet low-cost, high-performance requirements.

3GPP Release 16
At the TSG#88e Plenary meetings – ending July 3, 2020 – Release 16 was completed with both the Stage 3 freeze and the ASN.1 and OpenAPI specification freeze being approved.
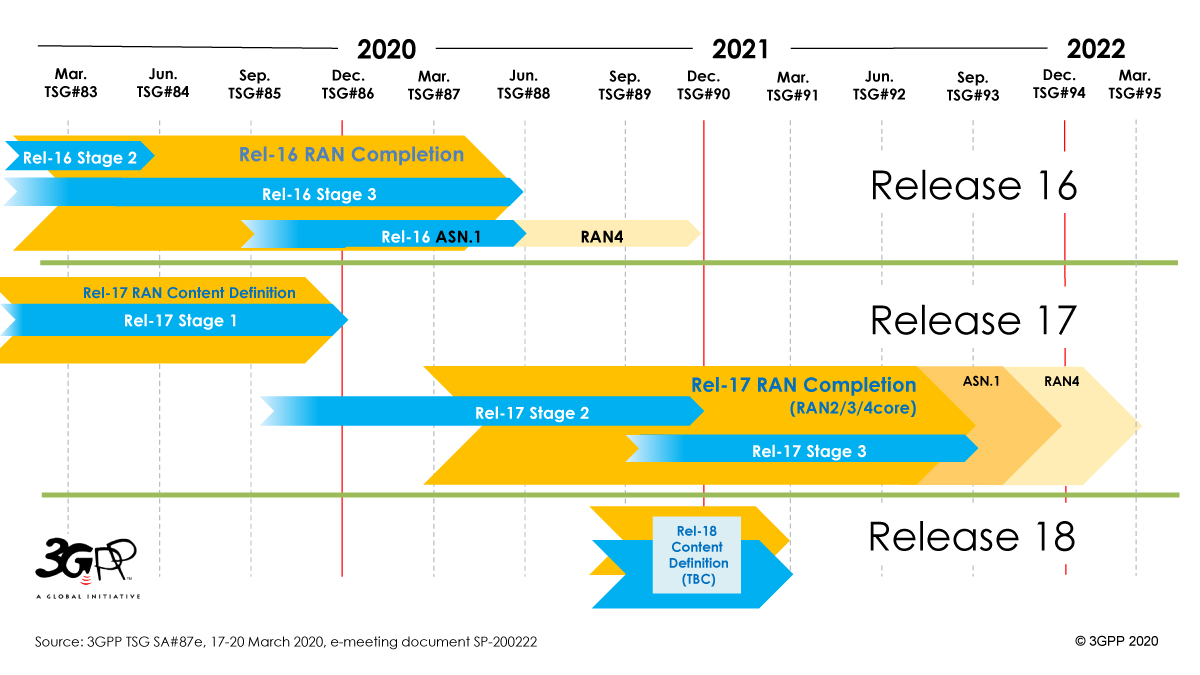
Release 16, the first step in the NR evolution, contains several significant extensions and enhancements. Some of these are extensions/improvements to existing features, while others are entirely new features that address new deployment scenarios and/or new verticals.
It is an important release for 5G. Many operators will use it as the reference release for their first adoption of a 5G Core (5GC). The 5G community is excited for the completion of Release 16 as the new core network will deliver a valuable set of enhancements to the Release 15 capabilities.
Release 16 features
- Cellular IoT support and evolution for the 5G system: Introduces a set of features to the 5GC similar to those introduced for EPC support of Cellular IoT in LTE (NB-IoT, LTE-M).
- Enhancement of URLLC support in 5GC: Adds various methods to support redundant transmission in the network for improved reliability and resiliency E2E. Covered under “Industrial IoT”.
- Enhanced support of vertical and LAN services: This is 3GPP’s official feature name, which introduces IIoT Phase 1.
- Enhancement to the 5GC location services: In Rel-15, location services were primarily for emergency call handling. Rel-16 adds support for commercial and IoT use and also support for non-3GPP access, as well as the possibility for positioning techniques using the cellular network transmissions on a standalone NR carrier.
- Architecture enhancements for 3GPP support of advanced V2X services: Provides support for the following use cases: vehicle platooning, advanced driving, extended sensors and remote driving.
- Enhancements to the 5G system service-based architecture: Improved support for service-based architecture with flexible service framework catering for the needs of various deployment models. Enablers to support a fully resilient 5GC, allowing both stateful and stateless implementations. Service framework and resiliency solutions are backward-compatible with Rel-15 network functions.
- Enhancement of network slicing: The UE NSSAA allows the service provider to outsource subscription management in wholesale scenarios. The UE is assigned to a slice-specific Session Management Function (SMF) after mobility from the EPS in “idle” or “connected” mode.
- Enhancing topology of SMF and User Plane Function (UPF) in 5G networks: Allows deployment of SMF/UPF/5G Access Network such that they are grouped into autonomous regions while ensuring session continuity when the UE moves between these regions.
- User data interworking, coexistence and migration: Enables independent scaling of Unified Data Management (UDM) and Home Subscriber Service (HSS) by using an open interface between them.
- Optimization on UE radio capability signaling: Optimizes the size of the information sent by the UE to the network to signal its capabilities in the EPS and the 5G System. Optimizes the size of the information stored in the network to identify UE capabilities. Optimizes the size of UE radio capability information in the UE context transferred in the network-function-to-network-function signaling messages.
- Enhanced IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) to 5GC integration: Aligns the IMS protocols to the 5G system service-based architecture approach by allowing use of HTTP instead of DIAMETER.
- Single radio voice continuity from the 5G system to 3G: Allows voice call continuity in mobile networks not deploying LTE but only 3G. Allows voice call continuity in holes of LTE coverage for mobile networks with both Voice over New Radio (VoNR) and Voice over LTE (VoLTE) enabled.
- System enhancements for Provision of Access to Restricted Local Operator Services by Unauthenticated UEs (PARLOS): Enables restricted local operator services as per FCC regulations for E-UTRAN (same as what was available in CDMA). Allows activation of a SIM card.
- 5GS transfer of policies for background data transfer: Policy control of background data transfer initiated at UE based on the time and location of the UE so that the 5G system can optimally use the control plane and/or user plane resources.
- MIMO enhancements.
- Two-step Random Access Channel (RACH): Introduces a shortened initial access procedure.
- Remote Interference Management (RIM) and Cross-Link Interference (CLI) Management: Introduces techniques for managing interference from distant cells in Time Division Duplex (TDD) networks in the presence of tropospheric scattering, as well as managing inter-operator interference.
- UE power saving.
- Multi-RAT dual connectivity and carrier aggregation enhancements: Introduces NR-NR dual connectivity, as well as various enhancements for LTE-NR dual connectivity and NR-NR carrier aggregation, especially to reduce delays.
- Mobility enhancements.
- IAB (Integrated Access and Backhaul).
- NR UE capability signaling optimization: Aims to reduce the overheads of UE capability signaling.
- Private network support.
