What is O-RAN Alliance?
O-RAN Alliance is a global alliance founded in 2018. As of June 2022, the O-RAN Alliance had 345 members and contributors (O-RAN Alliance only allows communication service providers as members, all other companies and entities are considered to be contributors). This includes communication service providers (CSP) and vendors, as well as academia and governmental institutions.

The O-RAN Alliance defines specifications in areas of RAN automation, cloudification, and disaggregation. The ambition of O-RAN Alliance is to enable an Open RAN by creating a multi-supplier RAN solution that allows for the separation – or disaggregation – of hardware and software with open interfaces and virtualization, hosting software that controls and updates networks in the cloud.
O-RAN ALLIANCE is committed to evolving RAN (Radio Access Networks) with its core principles being intelligence and openness. It aims to drive the mobile industry towards an ecosystem of innovative, multi-vendor, interoperable, and autonomous RAN, with reduced cost, improved performance, and greater agility.
What is the difference between Open RAN and O-RAN Alliance ?
Open RAN is an industry term for open radio access network architecture. It is a RAN that includes open interoperable interfaces and virtualization and is big data and AI-enabled.
O-RAN Alliance is an industry initiative for additional disaggregation, automation, and openness in RAN. Its main objective is to create global standard specifications. It can be considered a complement to 3GPP.
O-RAN ALLIANCE Streams
O-RAN ALLIANCE is active in 3 main streams:
-
Specification effort: Extending RAN standards towards openness and intelligence through 11 Working Groups (WGs).
-
O-RAN Software Community: Development of open software for the RAN (in cooperation with the Linux Foundation).
This community is partnering with the O-RAN Alliance and Linux Foundation to support the software development for an open RAN solution that is available to everyone. The community will align with the architecture and specifications that are created by the O-RAN Alliance working groups to create a working software solution to enable an open and intelligent 5G radio access network.
-
Testing & Integration: Supporting O-RAN member companies in testing and integration of their O-RAN implementations.
O-RAN Testing and Integration Focus Group (TIFG) defines O-RAN ALLIANCE’s overall approach to testing and integration, including:
-
Test & integration specifications.
-
Profiles to facilitate O-RAN productization, operationalization, and commercialization.
-
Approaches to meet general requirements.
-
Processes for performing integration and solution verification.
-
Criteria and Guidelines for Open Testing and Integration Centre
-
O-RAN Alliance workgroups and focus groups
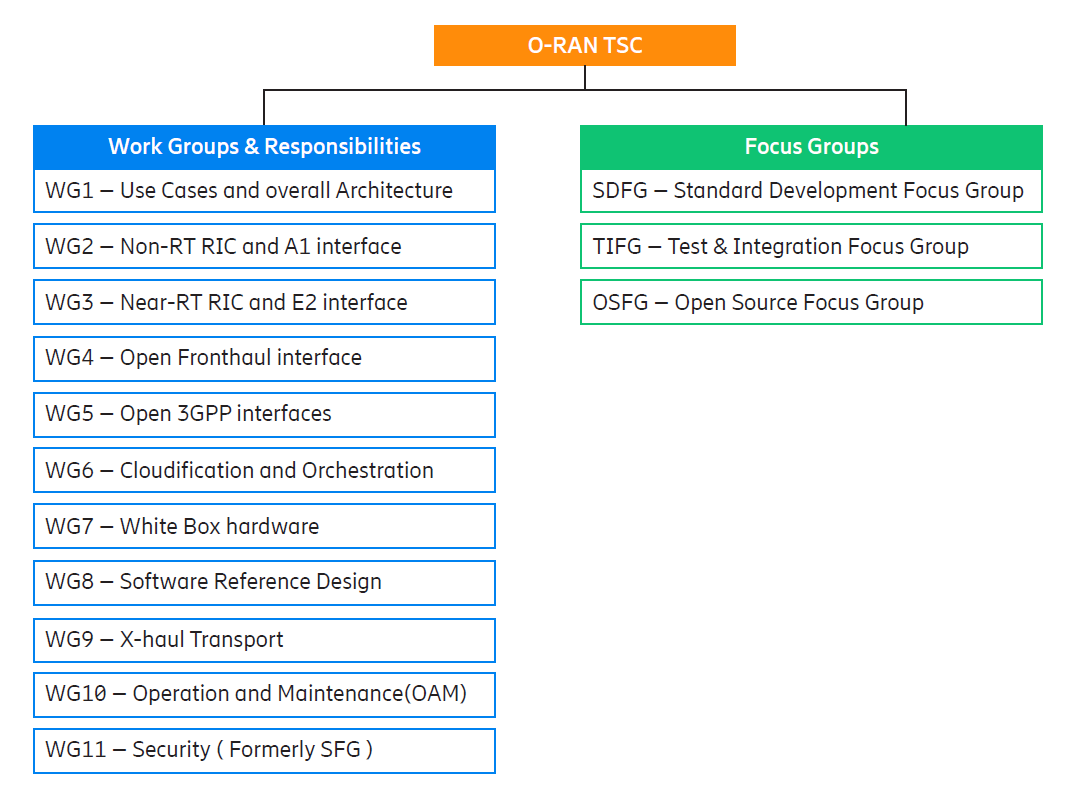
There are 11 work groups (WGs) and three focus groups (FGs). The Technical Steering Committee (TSC) supervises the technical workgroups which are responsible for O-RAN specification work. Each of the technical workgroups covers a part of the O-RAN architecture. Security is critical to the entire O-RAN architecture. Previously the Security Focus Group (SFG) was created to oversee the security aspects of the entire open RAN ecosystem. Naturally, SFG’s work encompasses all WGs. Focus groups do not normally engage on the O-RAN specifications, but with SFG, it is different. The SFG has published several technical specifications, and operates much like a WG, as a result of which, it was changed to WG11 (Security), Source of this explanation is Ericsson.
For more details about each Working Group, Please visit this article
O-RAN Alliance Automation, Interfaces, and Cloudification
- For network automation, the O-RAN Alliance is specifying two alternatives RAN Intelligent Controllers (RICs), Non-RealTime and Near-RealTime RIC. NonRT RIC is specified in the O-RAN Alliance WG2, while NearRT RIC is specified in WG3. The overall Service Management and Orchestration (SMO) architecture is specified in WG1.
- For RAN internal interfaces, the O-RAN Alliance has been working on the development of interoperable profiles for interfaces specified by 3GPP (especially F1, X2, and Xn interfaces) and on lower layer split (LLS). Interoperable profiles are developed in WG5, while LLS is developed in WG4.
- For cloudification, the O-RAN WG6 has two main activities. Firstly, it specifies the O2 interface that will be used to deploy, manage, and orchestrate the cloud infrastructure used in the RAN. Secondly, it also specifies how hardware (HW) acceleration can be implemented.
