Before discussing why we need an SMS Router, let’s understand the 1st figure when the mobile device sends SMS to another Mobile through the normal scenario without an SMS Router which means the communication is between SMSC and HLR.
The Normal Scenarios for Sending SMS:
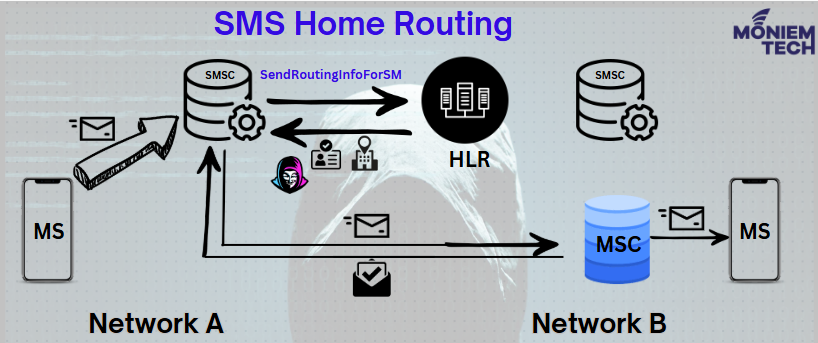
- The mobile sends the SMS to the SMSC.
- Since the SMSC does not know the location of the terminating subscriber, the SMSC requests this information from the HLR containing the information pertinent to the terminating subscriber.
- This is accomplished using the MAP-Send-Routing-Info-For-SM query message (SRI-For-SM).
- The terminating subscribers’ MSISDN is included in the SRI-For-SM to be used in the HLR query.
- After the lookup – the HLR returns a SRI-For-SM response to the requesting SMSC. At the MAP level, this message includes the Point Code (address) of the current MSC/VLR serving the recipient subscriber & IMSI of the recipient Subscriber.
What is the security threat here?
There are two main Security Concerns:
- Subscriber Tracking: Misuse of SRI for SMS requests can lead to unauthorized tracking of a subscriber’s location.
- SMS Spoofing and Fraud: Threat actors may exploit vulnerabilities in SRI for SMS to intercept or reroute SMS messages.
What are the Mitigation Actions?
There are many solutions including Home_Routing which ensures that sensitive messages, such as OTPs (One-Time Passwords), pass through the home network, where they can be monitored and protected, and enables the detection and blocking of spam or fraudulent messages.
The Role of SMS Router
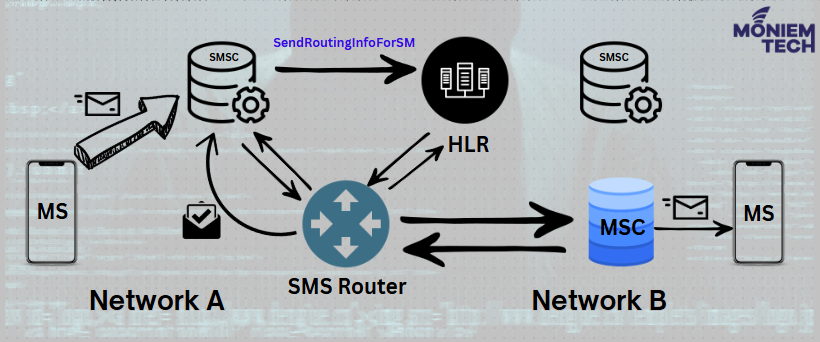
- Rather than sending the IMSI of the recipient subscriber the SMS Router inserts a Correlation_ID. This will keep the IMSI confidential.
- The SMS Router sends its address as serving the recipient subscriber rather than the subscriber’s location. This information forces the requesting SMSC to send the SMS Message to the SMS Router for delivery keeping the SMS Router in the SMS delivery path.
- This capability enables the SMS Router to perform value-added and security functions including the prevention of Spamming, Spoofing, and Faking.
The MT Correlation ID is a service element used only when the HPLMN of the receiving MS is using an SMS Router. It is used to correlate a Forward SM operation to a previous Info Retrieval operation.
Home Routing Bypass
When home routing is bypassed, SMS messages are delivered directly to the recipient’s serving network (MSC or SGSN) without passing through the home network. This bypass can occur due to:
- Misconfigured Network Elements: Incorrect configurations in HLR, MSC, or SMSC may allow direct routing.
- Exploitation of SRI for SMS:
- Attackers send SendRoutingInfoForSM (SRI for SMS) queries to retrieve the recipient’s IMSI and MSC addresses directly.
- Messages can then be sent to the recipient without passing through the home network.
- Weak Signaling Security: Lack of signaling firewalls or poor access control policies in SS7 networks can allow unauthorized SRI for SMS queries.
Implications of Home Routing Bypass
- Privacy Violations: Sensitive information, such as OTPs or banking alerts, could be intercepted.
- Revenue Loss: The home network may lose revenue as messages bypass its infrastructure.
- Spam and Fraud: Attackers could use bypassed routes to send unsolicited or malicious messages.
- Regulatory Compliance: Networks may fail to comply with regulations that require all messages to pass through the home network.
Mitigation Measures
- Signaling Firewalls: Implement SS7 firewalls to detect and block unauthorized SRI for SMS queries.
- Access Controls: Restrict access to critical network elements, such as the HLR, to trusted entities only.
- SRI Filtering: Ensure SRI for SMS requests are only allowed from legitimate SMSCs.
- Encryption: Use secure communication protocols to prevent interception of signaling messages.
- Network Configuration: Regularly audit and validate network configurations to prevent misrouting.
Conclusion
External networks send queries for subscriber locations and identities in the SMS delivery process. Providing this information to external networks poses a security risk as it can be used to launch a multitude of SS7-based attacks including location tracking, eavesdropping, DoS, and SMS spamming. The SMS Home Routing process permits the delivery of SMS by external networks while never disclosing real subscriber locations or identities.
