Wi-Fi is a key resource in the world communications ecosystem. Up to 90% of all mobile device traffic is carried on Wi-Fi. The 6 GHz band is a breakthrough that sets Wi‑Fi 6E and Wi‑Fi 7 apart from all earlier generations. They are the first to operate on 6 GHz, enabling more bandwidth, less interference, and better performance.
6 GHz Frequency Band Overview
- Lower band -> 5925–6425 MHz
- Upper band -> 6425–7125 MHz
- Full band -> 5925–7125 MHz
6GHz Band in GCC Countries
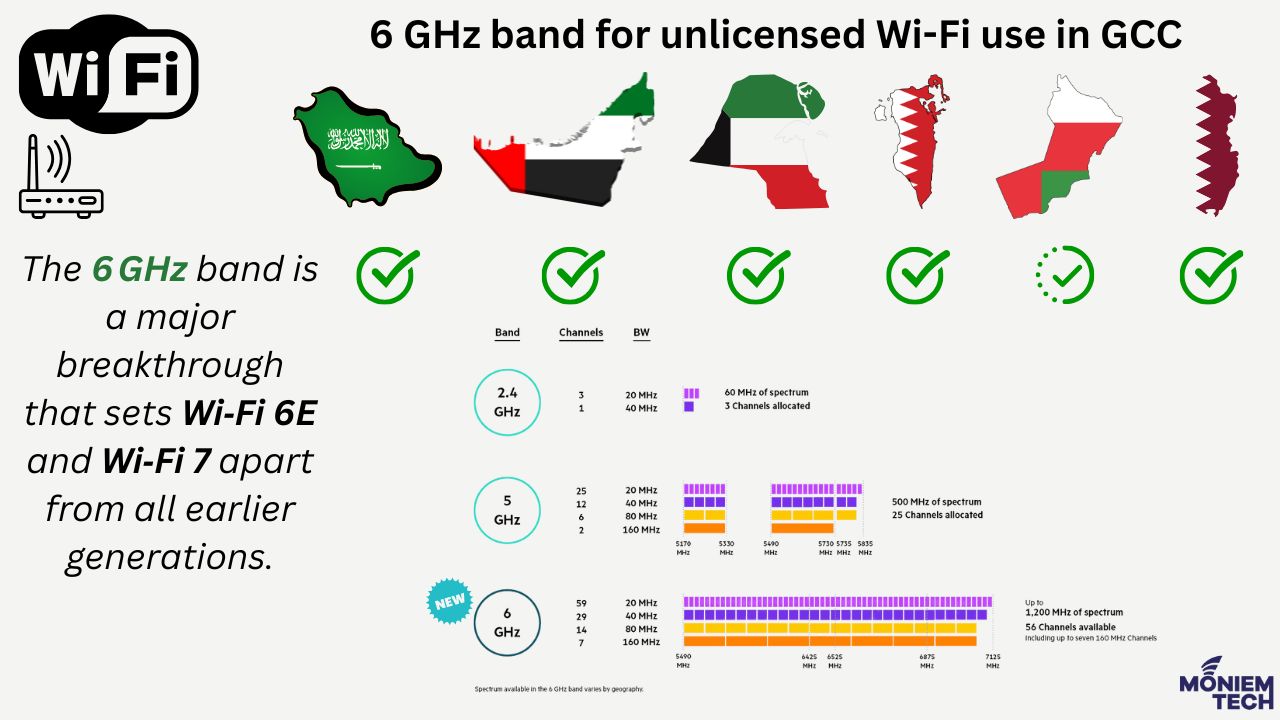
- Saudi_Arabia
- Saudi Arabia is the first country in the Middle East, Europe or Africa to designate all 1200 megahertz of the 6 GHz band for unlicensed use.
- UAE
- TDRA designated the 500 MHz radio spectrum of the 6 GHz band (specifically 5925-6425 MHz) to Wi-Fi for indoor use at an EIRP of 250 mW under class authorisation.
- Kuwait
- In May 2022, CITRA approved the amendments to the WiFi Regulations for a frequency range of 5925-6425 MHz, indoor use only and an EIRP value of 200mW.
- Bahrain
- In August 2022, Bahrain approved radio spectrum for faster Wi-Fi 6 technologies in spectrum ranges 5470 – 5725 MHz and 5925 – 6425 MHz for Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E applications.
- Oman
- Oman’s TRA launched a public consultation in April 2021 on the potential use of the 6 GHz band (5.925–7.125 GHz) for Wi-Fi technology. However, as of mid‑2025, no formal authorization has been granted for unlicensed operation anywhere in the 6 GHz band.
- Qatar
- On April 27 2022, Qatar’s Communications Regulatory Authority (CRA) issued a Class License for RLAN devices, specifically authorizing operation in the lower portion of the 6 GHz band (5925–6425 MHz).
Notes:
- Wi‑Fi 6E = Wi‑Fi 6 + new 6 GHz band.
- Wi‑Fi 7 = Wi‑Fi 6E + much faster speed, lower latency, MLO, and wider channels
In conclusion, the 6 GHz band marks a transformative leap for Wi‑Fi, empowering Wi‑Fi 6E and Wi‑Fi 7 to meet the growing demands of our hyper-connected world. By offering greater bandwidth, reduced congestion, and enhanced performance, these technologies are redefining wireless connectivity and ensuring that Wi‑Fi remains a cornerstone of the global communications ecosystem.
