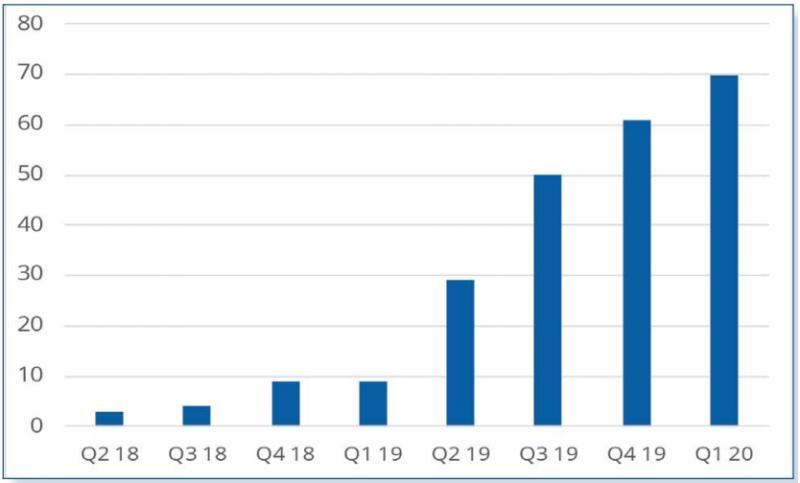
The Latest GSA’s Report for Q1 2020
As per GSA, the latest report for Q1 2020, 70 commercial 5G networks in 40 countries.
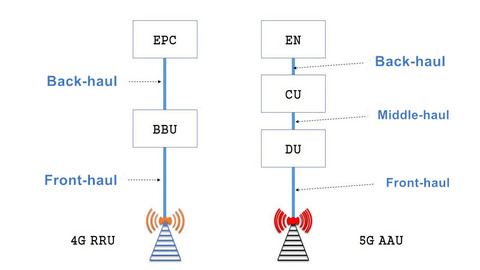
What Is CU-DU Function Split?
The main reason for CU-DU Split function is the high required front-haul transmission BW in 5G NR that may equal or exceed 160 Gpbs to support the user with a data rate of around 4 Gbps (Vs. 4G that needs 2Gpbs for the user with a data rate about 150Mbps). To resolve this issue, it’s mandatory to reduce this required transmission BW by moving some functions to DU. Versus the situation in 4G C-RAN, The digital processing unit has all functions from (PHY,MAC,RLC, and PDCP) and Radio equipment has RF functions.
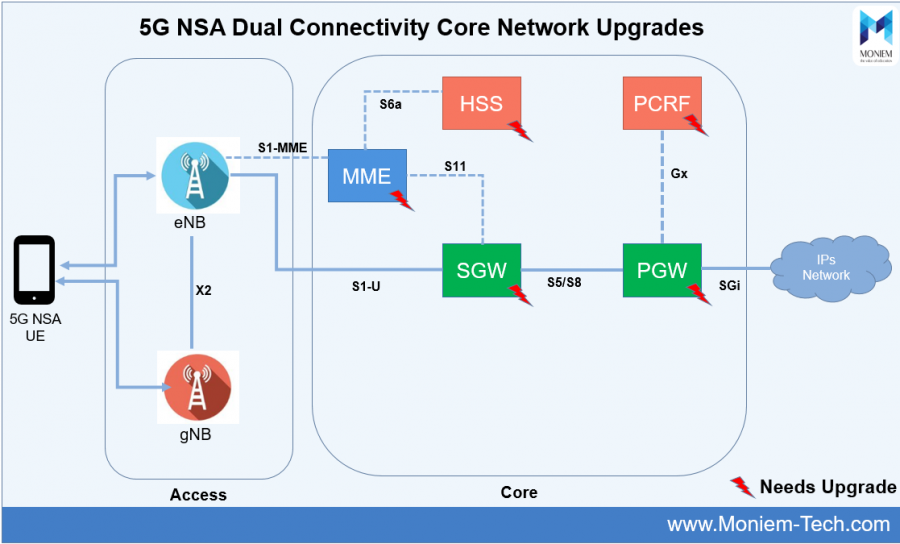
EPC Core Upgrade for 5G EN-DC
What Is the Difference between 4G C-RAN and 5G C-RAN?
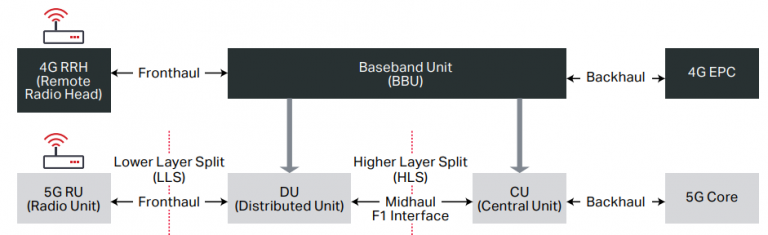
As per MTC Consulting, A typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station. According to Huawei data on RRU/BBU needs per site, the typical 5G site has power needs of over 11.5 kilowatts, up nearly 70% from a base station deploying a mix of 2G, 3G, and 4G radios. 5G macro base stations may require several new, power-hungry components, including microwave or millimeter-wave transceivers, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), faster data converters, high-power/low-noise amplifiers, and integrated MIMO antennas.
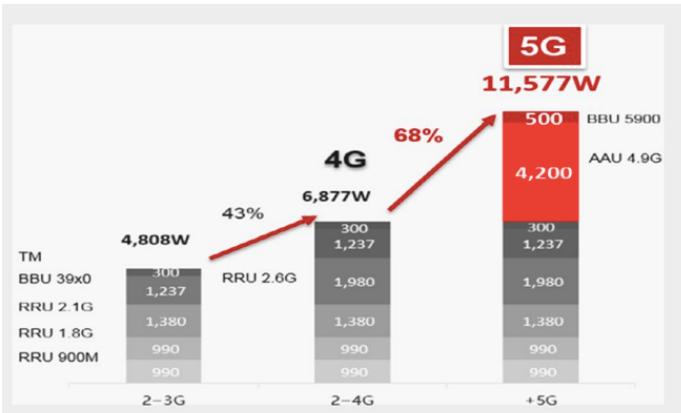
EPC with SDN and NFV
Switching from traditional EPC with
- Complex functionality in HW appliances.
- Difficult to scale, inflexible and Expansive.
= EPC with NFV
- Flexible, salable software appliances.
- Use commodity high-end servers, data centers.
= EPC with SDN
- Flexible software-based control plan.
- Commodity SDN Switches in the data plan.
Did You Know?
Neil_Papworth is the sender of the First text message (SMS) On December 3rd, 1992. He was working as a developer and test engineer at Sema Group Telecoms (that was acquired by different companies to be acquired now by Mavenir ) in a team developing a Short Message Service Centre (SMSC) for their customer, Vodafone UK in Newbury. He sent the world’s first text message, on 3 December 1992, at the age of 22. It was sent from a computer. The message was “Merry Christmas”, and was sent to Richard Jarvis, a director at Vodafone. Richard Jarvis received the message on an Orbitel901 handset.

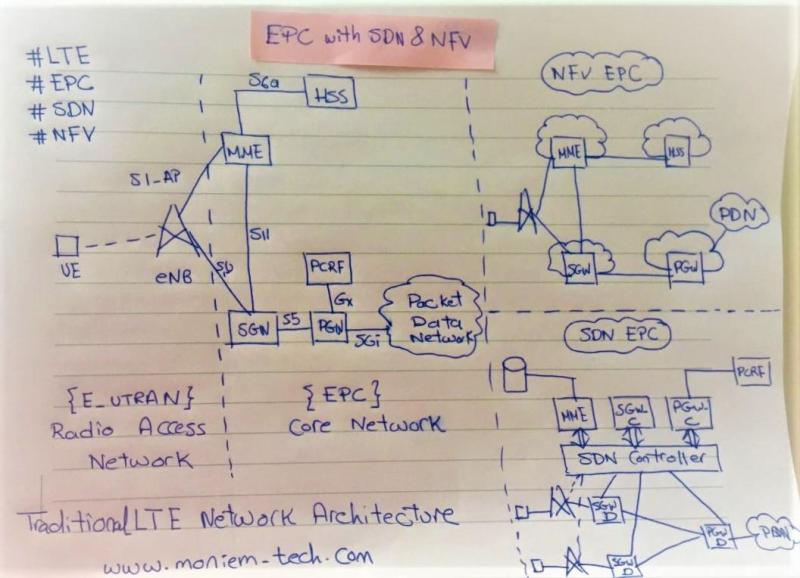
To serve the three use cases, eMBB, MTC, and URLLC, the required flexibility of the Radio scheme is now obtained by allowing different numerologies to be applied in the same 5G NR Channel.
Here, It’s obvious that some numerologies have a shortened symbol duration, which perfectly fits the QoS requirements for URLLC.
On the other hand, longer symbol durations and thus narrower subcarrier spacings allow a large Cell Size can combat along with delay spread.
Some of the 5G Spectrum Notes
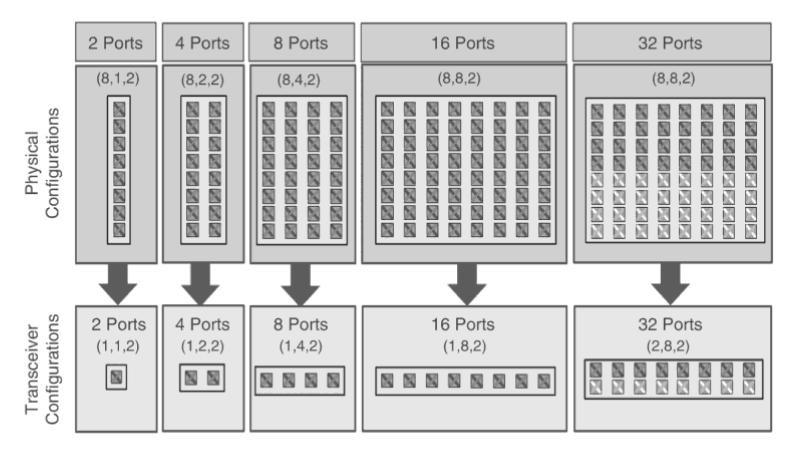
Antenna Array
Physical Array Configurations & TXRU (Logical) Configurations.
Array Configurations
- 8 rows of cross-pol elements in all cases.
- 2, 4 or 8 columns.
- Column spacing: 0.5 wavelength.
- Row spacing: 0.8 wavelength.
Physical Antenna Elements
- Azimuth Beamwidth=65degrees
- Elevation Beamwidth=65degrees
- Element gain = 8 dBi
- Front2Back = 30 dB
TXRU Mapping
- Sub-array methodology
- Within a column: statically aggregate (e.g., at RF) disjoint selections of adjacent co-pol elements
- Aggregate for a fixed electrical downtilt
- Consider 1,2,4,8 Rows of TXRUs per column
Source: Nokia
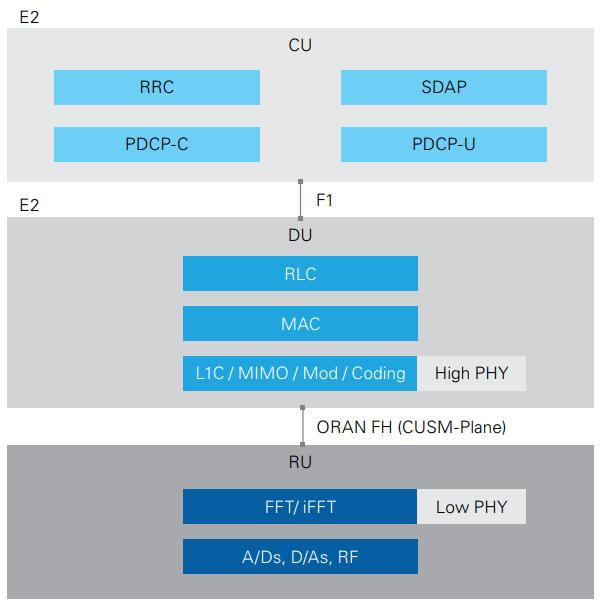
The O-RAN alliance, or O-RAN, focuses on achieving an unprecedented level of openness in the way 5G RANs are built.
In Release 15, the 3GPP identifies three distinct gNodeB functions: Centralized Unit (CU), Distributed Unit (DU), and Radio Unit (RU).
Option 7-2 which splits the physical layer (PHY) into a high-PHY and a low-PHY.
For option 7-2, the Uplink (UL), CP removal, fast Fourier transform (FFT), and prefiltering (for PRACH (Physical Random Access Channel) only) functions all occur in the RU and the rest of the PHY is processed in the DU.
For the Downlink (DL), the inverse FFT (iFFT), CP addition, precoding functions, and digital beamforming (if applicable) occur in the RU, and the rest of the PHY processing happens in the DU.
For new 5G RAN architectures (called NR-RAN), the 3GPP has defined and standardized on a new interface, the F1 interface, for communication between the CU and the DU.
Source: NI
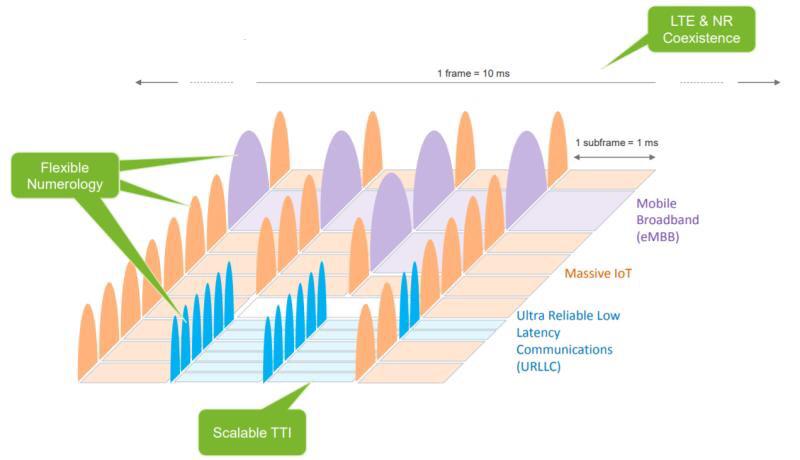
5G NR Frame Structure
5G NR adopts OFDMA, which is the same scheme used in LTE.
To adapt to services requiring low latency and to enable the use of higher frequencies, NR supports higher subcarrier spacing of 30, 60, 120, and 240 kHz based on the LTE subcarrier spacing of 15 kHz. Image
Source: InfoVista
Lufthansa pilots standalone 5G networks in the aircraft maintenance industry
It is working with Vodafone and Nokia to test its own private 5G networks on two separate projects.
One enables clients to remotely join the airline’s engineers in real-time inspections of engine parts; the other project applies live AR/VR to overlay cabin interior designs onto a real empty fuselage, allowing engineers to check the design and position of every component.
Actually I like to see 5G beyond connectivity and especially in the verticle industries.

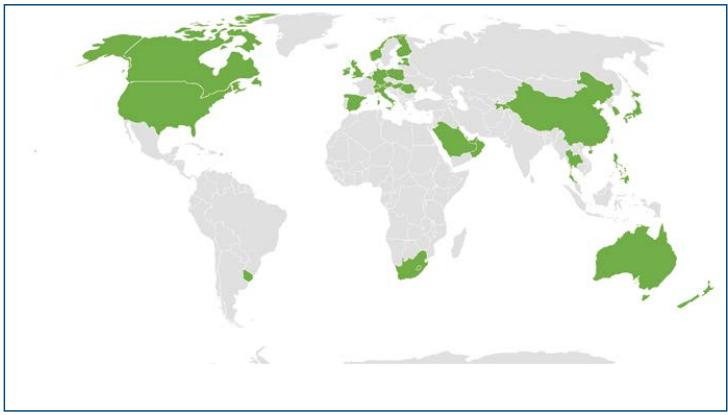
How Many Countries Launched 5G Commercially?
Till April, There are 73 operators in 41 countries that have launched one or more 3GPP compliant 5G services up from 63 operators in 35 countries in March.
Did You Know?
There’s a momentous shift happening in the industry with a move to break open 4G fronthaul networks. While based on a published Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) specification, these fronthaul networks ended up being closed and proprietary.
MNOs were forced to buy RRHs and BBUs from the same vendor and to transport fronthaul traffic over costly, and often unavailable, dark fiber due to CPRI’s very high (and inefficient) capacity and stringent latency requirements.
With 5G – this can and will change.
FCC Approves Wi-Fi 6E, So What Is Wi-Fi 6E?
On April 23, 2020, The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has approved its proposal to open up the 6 GHz band for unlicensed use, creating a new range of 1,200 MHz (5.925–7.125 GHz) for Wi-Fi services.
So What is WiFi6E?
What is the difference between WiFi6 and WiFi6E?
What are the Benefits?
Are there any WiFi 6E supported devices or Chips?

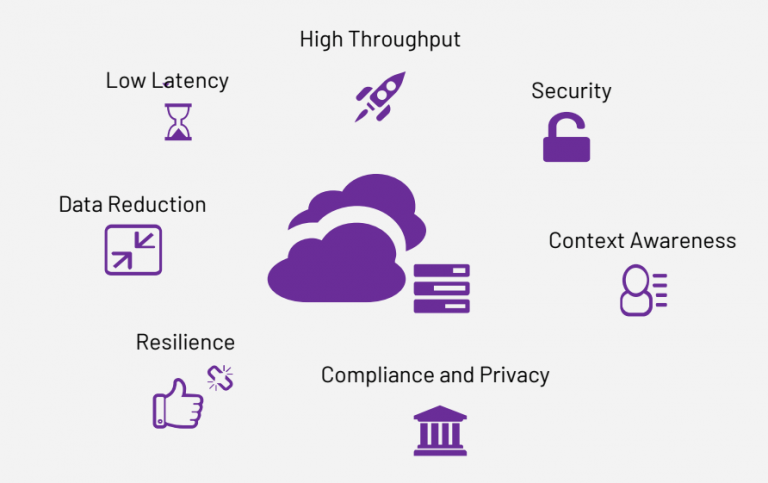
What Are the Edge Computing Benefits?
The benefits of reduced latency, improved throughput, better security, and isolation along with data reduction and context- and location-awareness make edge computing a compelling area of infrastructure investment for CSPs.
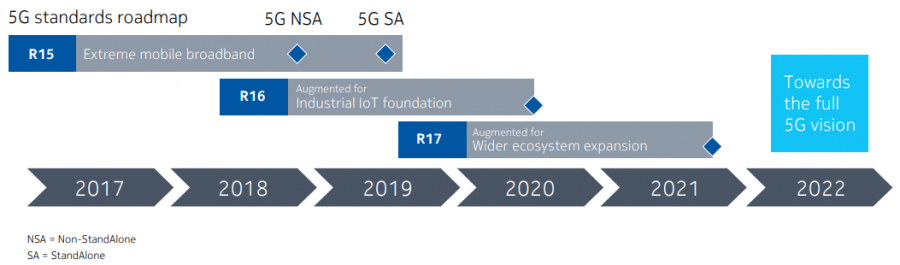
5G Releases 16 and 17 in 3GPP
The US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) took the decision to allocate spectrum in the 6 GHz band for unlicensed use (e.g. Wi-Fi).
This will bring enormous opportunities for the industry:
- An additional 1200 MHz of spectrum will now be available, the total spectrum for Wi-Fi has now tripled!
- Ensuring that Wi-Fi remains an important technology, moving forward with an ever-increasing capacity to support new types of devices and complement future 5G services.
There are some regions that may not be able to allocate as much spectrum as in the USA.
The new Wi-Fi 6 standard has the same scheduling mechanisms as cellular OFDMA.

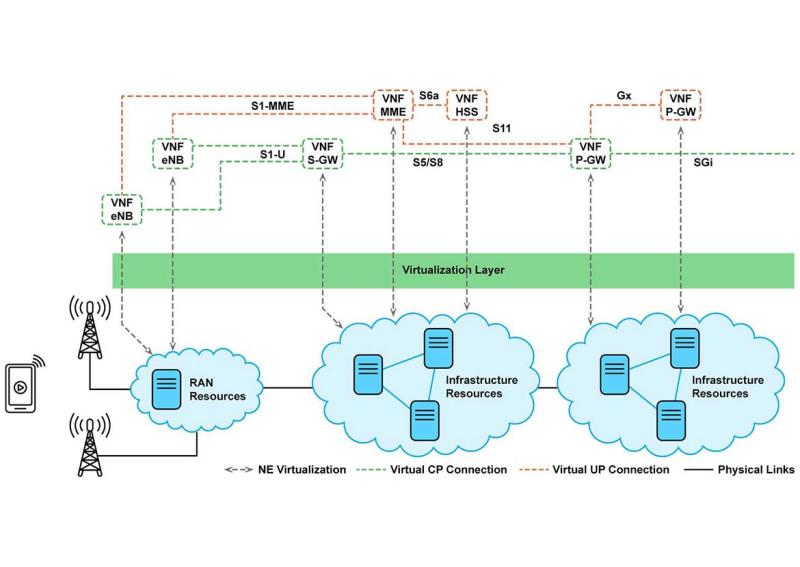
By virtualizing the 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G RAN, mobile operators can now reduce the cost of all generations of deployments, from 2G to 5G.
They can then deliver 5G coverage by making deployments easy and affordable to install and maintain while sustaining a high quality of service for customers.
Software-based ALL IP network architecture enables operators to utilize the benefits of advanced 5G RANs without deploying the 5G core and selecting the 5G core migration path that most cost-effective and makes business and operational sense.
Source: Parallel Wireless