VoNR is IMS based voice services that use 5G as the access network (as opposed to LTE and VoLTE)
Introduction
Voice over New Radio (VoNR) is the IP Multimedia System (IMS) based voice calling services that use the 5G network for its source of Internet Protocol (IP) voice processing.
The New Radio network communication is the 5G radio access technology and the advanced & updated form of 4G radio access technology.
The mobile voice is a legacy service that continues to exist in each new mobile generation.
Two main types of voice services that will be available over 5G mobile networks:
- Carrier-Grade Voice Service which has strict QoS support and does not belong to the public Internet Voice over New Radio (VoNR) or Vo5G.
- OTT Voice Services will continue to exist in 5G networks and they will continue to be provided through the mobile Internet access on the best effort principle by using network neutrality (e.g., Viber, WhatsApp, Skype, and others).
Is Voice important to 5G?
5G is driven by the ever-increasing need for higher data speeds and new services But the voice also important for
- High 5G data speeds in smartphones.
- Support for new 5G specific use cases.
- CS legacy phase-out.
What Happens to VoNR?
3GPP has specified that 5G uses the 4G voice/video communication architecture and still provides voice/ video communication services based on the IMS.
One may note that VoLTE and VoNR are different access modes for IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) voice/video communication services.
So the typical scenario will be as below:
The voice on high frequencies
- Most initial 5G deployments are using the medium to high-frequency bands (New bands for higher data speeds).
- Challenges with the voice on high frequencies
— High free-space propagation loss.
— High diffraction loss.
— High wall penetration loss. - Solutions to overcome 5G coverage issues
— Dual connectivity with a lower 4G band.
— Fallback or handover to a lower 4G band.
— Carrier aggregation with a lower 5G band.
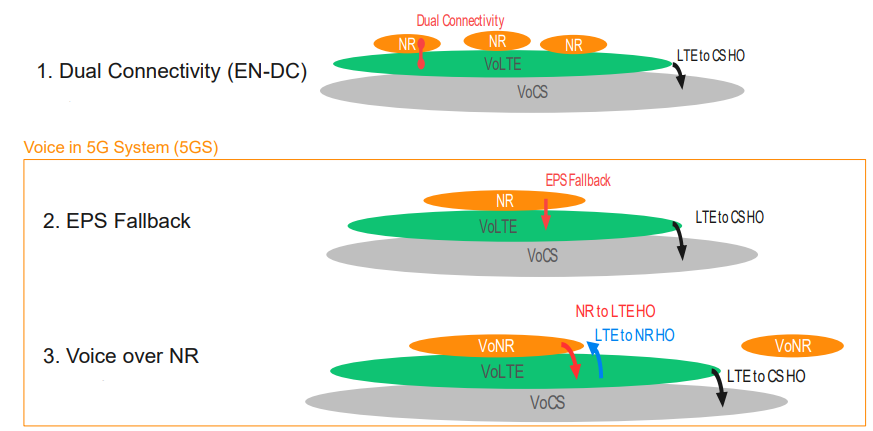
5G Voice Evolution steps
There are 3 steps to reach VoNR as below
- Dual Connectivity (EN-DC).
- EPS Fallback.
- Voice over NR.
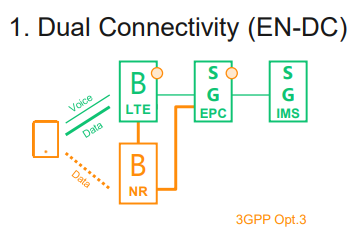
1. Dual Connectivity (EN-DC)
This is the first option to deliver the voice service or the first time to market.
• LTE for voice while using NR as a data boost.
• Data over NR may optionally be stopped during calls in order to ensure enough uplink power for voice over LTE on cell edges.
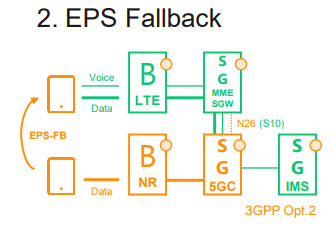
2. EPS Fallback
NR for data but falling back to LTE (for voice and data) when making or receiving calls
• Data over NR may optionally be reestablished after EPS-FB (with ENDC).
• EPC and 5GC with N26 interworking and IP address preservation in 5GC.
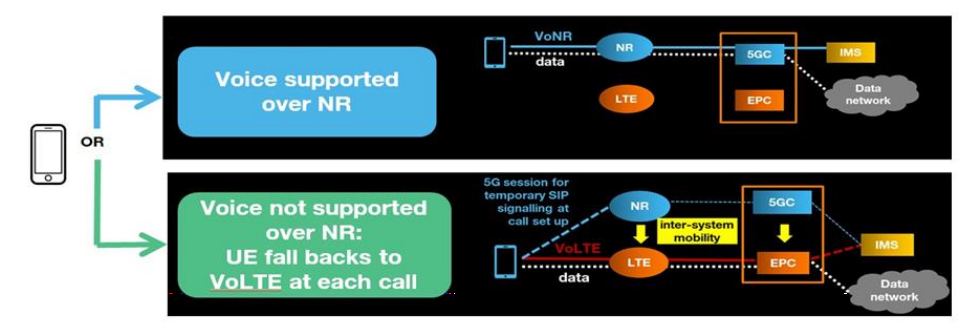
EPC Fallback can be triggered when a UE initiates an IMS voice call while connected to the 5G core network using the New Radio (NR). It requires the 5G core network to have connectivity to IMS.
The Fallback procedure moves the UE onto a 4G core network using EUTRA, So the 4G core network also has connectivity to the IMS so the voice call setup can then be completed.
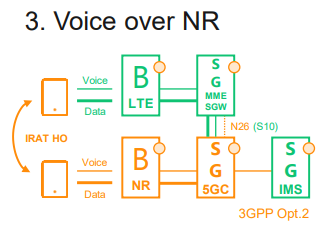
3. Voice over NR
This is the target step when 5G be matured enough
• NR for both voice and data.
• NR dimensioned for voice coverage.
• Seamless handover between 5G and 4G (and WiFi)
– No handover/fallback from 5G to CS.
Voice Solutions in 5G Stand-Alone (SA)
There are two solutions as we mentioned on the previous part, EPC Fallback and 5G over New Radio. there’re some notes regarding the two solutions as below.
Two key factors of voice in 5G SA were tested (in Orange 5G SA Trail) with or without N26 interface (between AMF & MME):
• The impact of 5G-4G mobility procedure on Voice Service
During a VoNR call, when 5G coverage is no more available, the call has to be seamlessly moved to 4G.
With N26 interface voice interruption time is around 70ms and Without N26 interface, the interruption time is 700ms
(the recommended limit for a voice call = 300ms)
• The impact of EPS Fallback (EPS-FB) on Call Set up Time (CST)
EPS-FB triggers inter-system Hand Over during call establishment which impacts the CST, With EPS-FB, the Call Setup Time is around 1s more than with VoNR (with N26) and still slightly increased without N26 (+ 0.5s).
References
- ITU.
- 3GPP.
- Ericsson.
- Orange.
Also, you can read more about:
