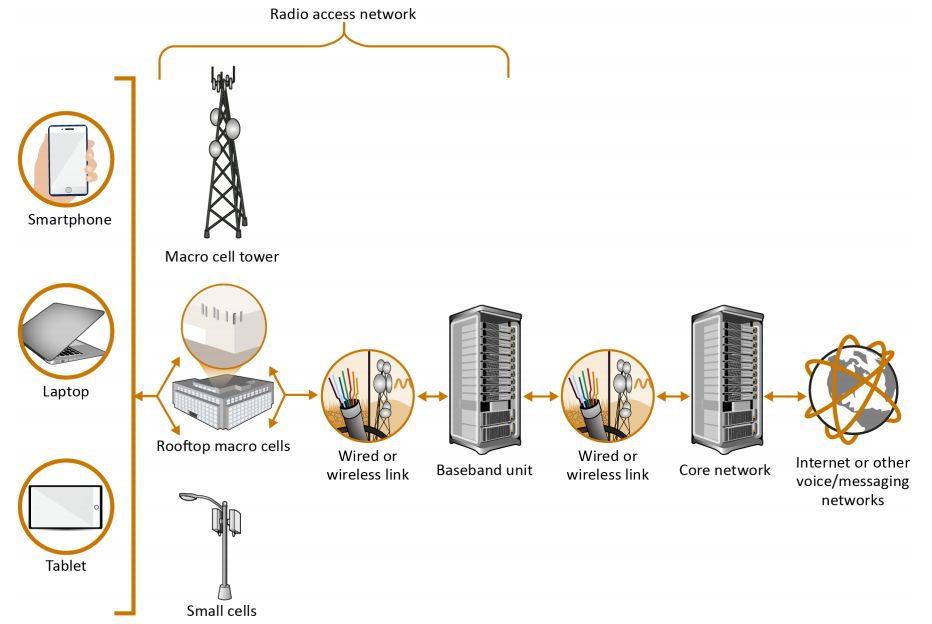
- The device connects over the Radio Access Network (RAN), which defines and manages the radio link between the customer device and the rest of the network.
- The RAN comprises cellular base stations (BTS in 2G, NodeB in 3G,eNodeB in 4G, and gNB in 5G), wired or wireless links, and a baseband unit that processes the radio signals and manages interference.
- Base stations for the networks include traditional macro cell towers and rooftop installations as well as small cells, which can also be installed on utility poles or streetlamps to provide service to a smaller area.
- The hardware and software used to connect devices wirelessly to the baseband units are known as RAN, which includes LTE for 4G networks and “New Radio” for 5G.
- Once a signal from the customer’s device reaches the base station, it is transmitted over a wired or wireless link to the baseband unit. The baseband unit connects over a wired or wireless link to the Core network, which manages the RAN and routes each connection to outside services, such as the internet, a landline, or back out through the RAN to another wireless device.
Nowadays, there’s a shift to de-couple Software and Hardware in RAN & Core domain with some booming words like #OpenRAN, #CloudNative, #VNF, #SDN, and #Cloudification.
