The journey started with 2G and 3G, where Voice was the leading service, and the main protocols were SS7 and SIGTRAN (Signaling Transport).
At this time, the primary Firewalls are:
- SS7/SIGTRAN Firewall: Its functions are national/international interconnect protection with different policies and detection patterns in real-time.
- GTP Firewall: The functions are GTP Packet binary checks and connectivity policies.
In 4G, networks became data—and media-centric and needed signalling to support smartphones and Apps. Here, Diameter is the main protocol, along with the introduction of VoLTE and SIP Protocol. Currently, the main firewalls are:
- Diameter Firewall: This is for LTE interconnection protection and AVP policies.
- SIP Firewall: For SIP Policies, SIP payload control and multi-channel authentication.
Finally, In 5G, network signalling is no longer a separate network like SS7 or Diameter. Signalling shares the Control Plane with all other Inter-Process Communications using HTTPS/HTTP/2 protocols. So, the main firewall:
- SEPP Firewall: For NGxC Interconnect protection and HTTP/s payload control.
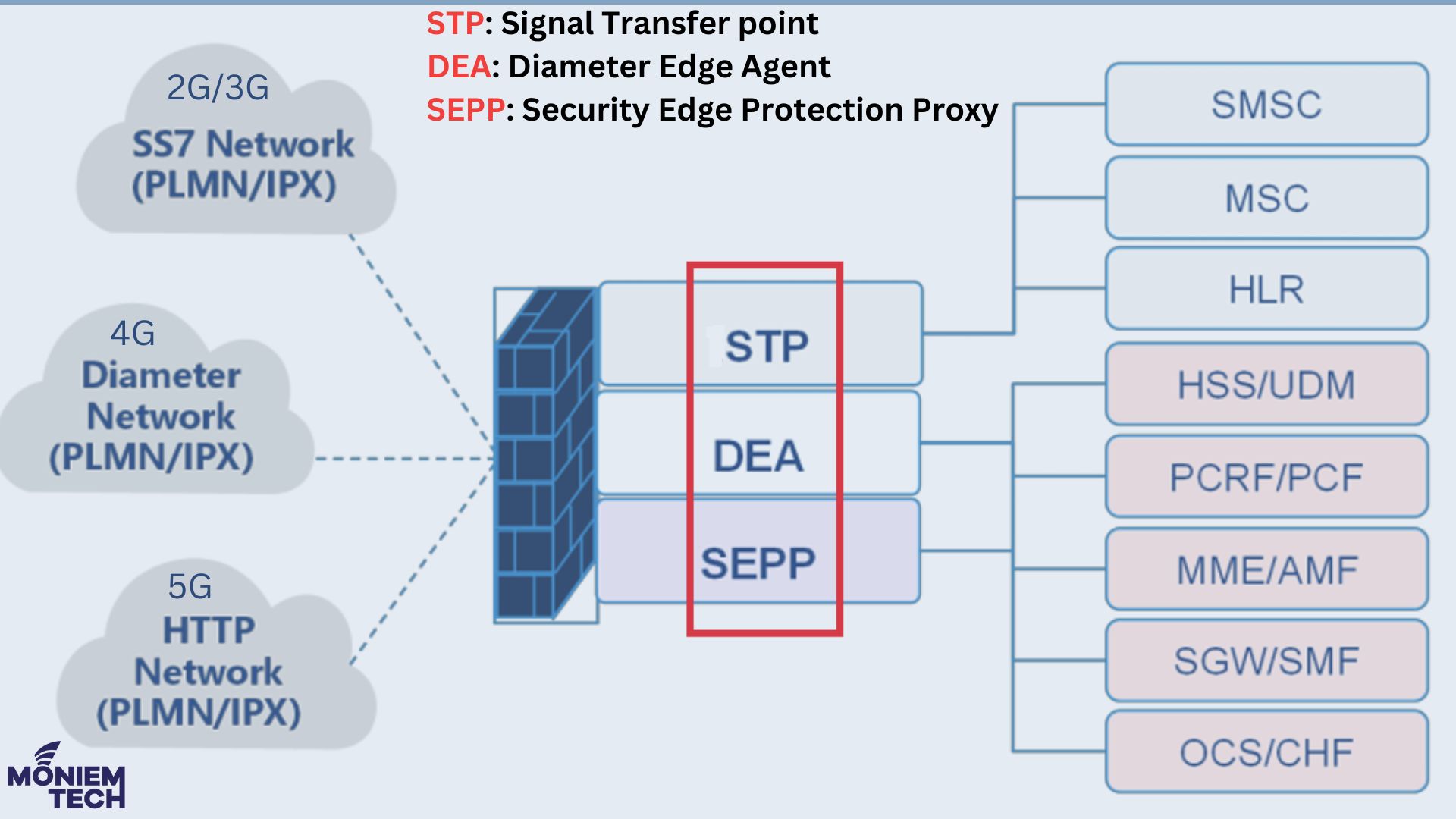
Summary of Evolution:
- SS7 (2G/3G) → Uses STP (Vulnerable to security risks).
- Diameter (4G) → Uses DEA (Improved security, but still has vulnerabilities).
- 5G Core (5GC) → Uses SEPP (Strongest security with encryption, authentication, and integrity protection).
Almost all vendors are moving towards a Unified Signaling Firewall to cover all signalling firewall rules in one solution.
