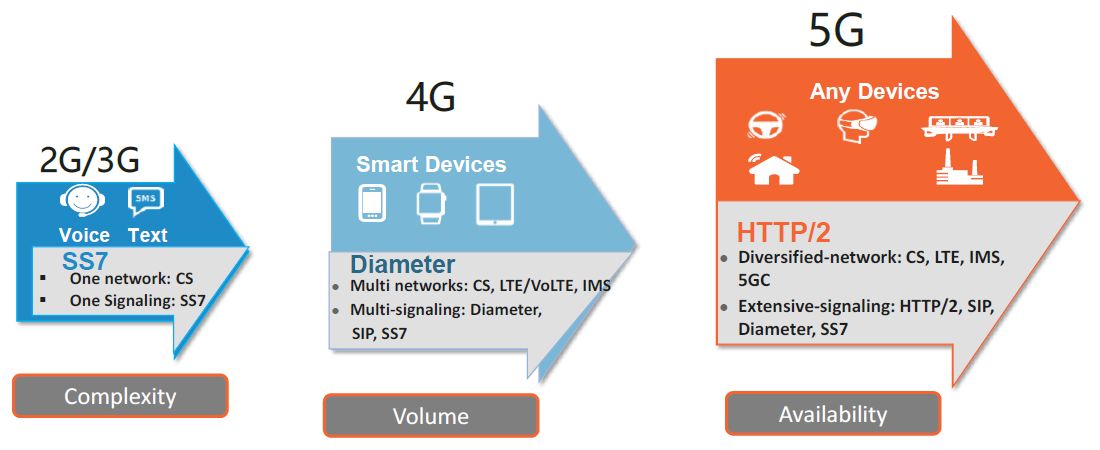
?In 2G and 3G, voice and text were the main services based on SS7 signaling. In these networks service availability was the priority. The Signal Transfer Point (STP) was the node that routed signaling messages.
?In 4G, networks became data and media-centric and needed signaling to support smartphones and Apps. Signaling volume grew to support these Apps using Diameter. Diameter signaling was controlled by the Diameter Routing Agent (DRA) and Diameter Relay Agents that performed routing and load management for Diameter signaling traffic.
?In 5G, 5G adopts HTTP/2 as an application layer protocol, meaning all the network entities in the control plane will communicate with each other using HTTP/2. Legacy protocols like GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTPv2) and DIAMETER are reserved for 4G/5G interworking. 5GC now adopts a new Service Based Architecture (SBA) where control plane communications between Network Functions (NFs) are implemented using RESTful APIs with HTTP/2 methods.
Why must we add a new signaling protocol in 5G?
- In 5G the network must support not only all these earlier services but many new high bandwidth, low latency applications, and massive machine-to-machine communications as well as handling complex interworking across multiple domains.
- 5G SA needs to handle the massively increased signaling transaction volume that 5G generates on the Control Plane. A volume now projected to be at least two orders of magnitude greater than operators have experienced with Diameter.
- 5G signaling must facilitate real-time interworking with legacy SS7 and Diameter to ensure seamless 4G, 3G, and 2G service interoperability.
How signaling is changed from 5G Release 15 to Release 16?
- In the 3GPP Release15 version of 5G signaling NFs simply sent direct discovery requests to the NRF. An approach that operates satisfactorily for trials and small network deployments.
- In 3GPP Release16 the Service Communication Proxy (SCP) has now been introduced to allow the Control Plane network to handle and prioritize massive numbers of requests in real-time.
- 5G SCP becomes the control point that mediates all signaling and Control Plane messages in the network core. SCP routing directs the flow of millions of simultaneous 5G function requests and responses for network slicing, microservice instantiation or edge compute access.
Interworking and Roaming Threats
Compared to 4G, roaming in 5G uses new protocols that provide greater flexibility and unknown threats. The embedded security at 5G roaming links is addressed in the following roaming concerns in the 5G architecture.
- The Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) node has been added to the 5G architecture to terminate signaling communications between PLMNs (Public Land Mobile Network) over inter-exchange/roaming links.
- The interconnection model will be comparable to today’s 3G and 4G networks’ SS7 or DIAMETER connections. However, on inter-exchange/roaming links, the application layer protocol like HTTP/2 will enable encryption.
- The incorporated application layer encryption at the SEPP will defend against the SS7 and DIAMETER protocols’ known inter-exchange/roaming weaknesses.
